NUMA-aware Scheduling
Feature Overview
The non-uniform memory access (NUMA) architecture has become increasingly prevalent in modern high-performance computing and large-scale distributed systems. In this architecture, memory is allocated to multiple nodes (NUMA nodes), each with its own local memory and CPUs. This design helps reduce memory access latency and improves system performance. However, the complexity of the NUMA architecture also introduces challenges in system resource management, especially in multi-task and multi-threaded environments. To fully leverage the benefits of the NUMA architecture, refined management and monitoring of system resources are essential. Through an intuitive graphical interface, visualized NUMA resource monitoring provides real-time insights into the allocation and utilization of NUMA resources. This enables users to better understand and manage these resources, improving system performance and resource utilization. In containerized clusters, resource scheduling is typically handled by various schedulers. This feature provides unified management of schedulers, such as Volcano.
Applicable Scenarios
This feature is applicable to the following scenarios: When deploying workloads, you may require cluster-level scheduling capabilities. After workloads are allocated to nodes, you may want to view the allocation details and apply different optimization strategies based on the allocation.
Supported Capabilities
- NUMA topology: The topology of NUMA nodes in the system is visually displayed, including CPU and memory distribution on each node. Connection relationships between nodes and access latency are displayed.
- Real-time resource monitoring: CPU usage for each NUMA node is displayed in real time, including utilization and idle status. Memory usage for each NUMA node is displayed, including total, used, and available memory.
- Detailed resource information: Detailed resource information about each NUMA node is displayed, such as the CPU list and memory capacity. CPU and memory allocations for each container on NUMA nodes can be viewed.
Highlights
- Visualized NUMA topology: A visualized topology of the system's NUMA nodes is provided, clearly displaying the physical connections between them.
- Real-time resource monitoring: CPU and memory usage of NUMA nodes are updated in seconds, delivering real-time performance monitoring.
- Refined container resource management: Resource allocation for each container on NUMA nodes can be precisely located.
- Compatible with various schedulers and unified management: Mainstream container orchestration schedulers such as Volcano are compatible and a unified NUMA resource management API is provided.
Restrictions
Both NUMA-aware scheduling and NPU Operator use Volcano. However, they use Volcano of different versions, which may cause conflicts. Therefore, they cannot be used together.
Implementation Principles
Kubernetes and the resource collectors are underlying topology–aware and can be configured to use cluster-level schedulers for resource allocation. You can configure scheduling policies on the frontend interface and monitor the current topology. The following figure shows the logical architecture of this feature.
Figure 1 Implementation principles
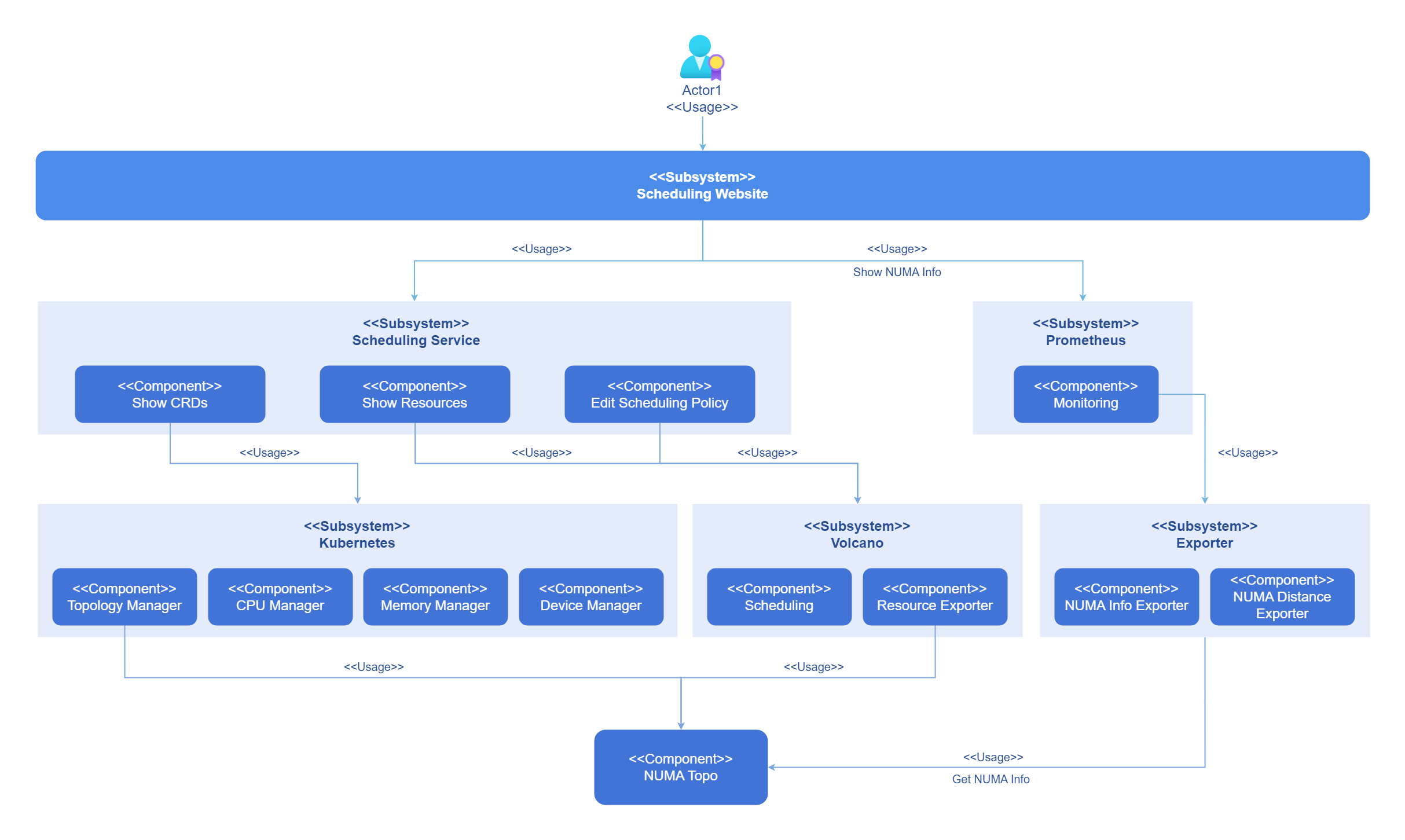
Before the introduction of the Topology Manager, the CPU Manager and Device Manager in Kubernetes make resource allocation decisions independently of each other. This often results in CPUs and devices being allocated from different NUMA nodes, causing additional latency. The Topology Manager provides Kubernetes with an API named Hint Provider to send and receive topology information, enabling optimal allocation decisions based on the specified policy.
Figure 2 NUMA allocation
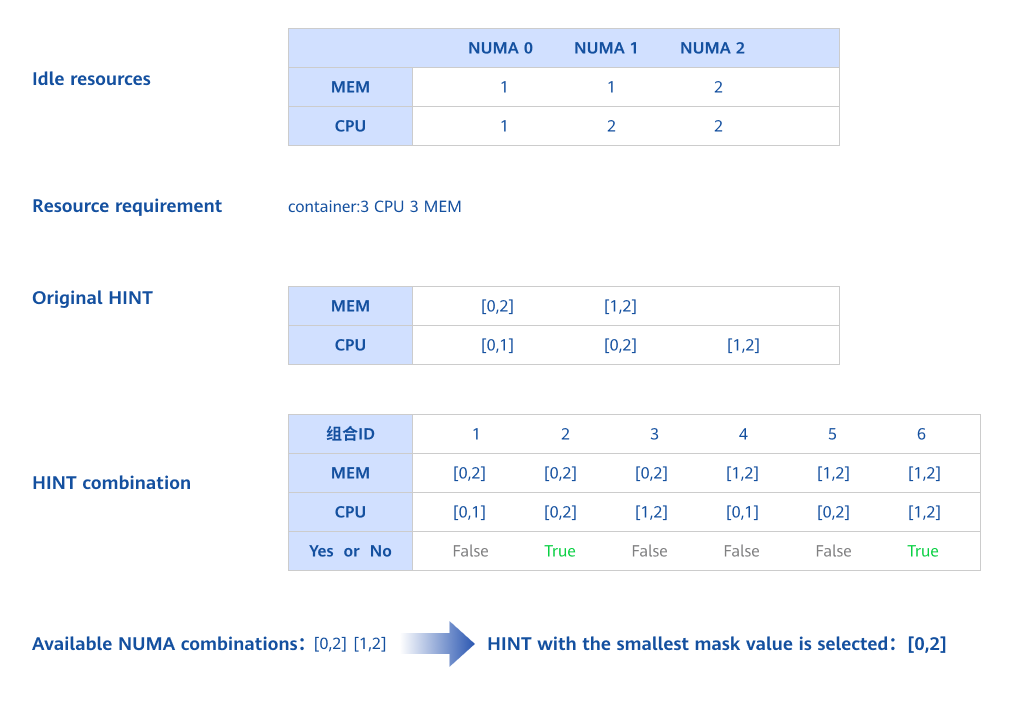
Kubernetes supports NUMA affinity settings for both CPU and memory. This requires configuring the CPU management and topology management policies. Using the Topology Manager's hint algorithm, Kubernetes ensures that allocated CPUs and memory reside on the same NUMA node.
The Topology Manager provides two distinct alignment options: scope and policy. The scope option defines the granularity at which you would like resource alignment to be performed, either at the pod or container level. The policy option defines the actual policy used to carry out the alignment, for example, best-effort, restricted, single-numa-node, or none.
Table 1 Expected topology-aware scheduling behaviors
| Volcano Topology Policy | Node Scheduling Behavior | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Filter nodes with the same policy. | 2. Further filter the node whose CPU topology meets the policy. | |
| none | No filtering behavior is performed:
| - |
| best-effort | Filter the nodes whose topology policy is also best-effort:
| Best-effort scheduling: Services are preferentially scheduled to a single NUMA node. If a single NUMA node cannot meet the requested CPU cores, the services can be scheduled to multiple NUMA nodes. |
| restricted | Filter the nodes whose topology policy is also restricted:
| Restricted scheduling:
|
| single-numa-node | Filter the nodes whose topology policy is also single-numa-node:
| Services can only be scheduled to a single NUMA node. |
The Kubernetes scheduler is not topology-aware and does not ensure that the node selected for the pod has an idle single NUMA node at the scheduling layer. As a result, the pod may fail to start. To solve this problem, Volcano supports NUMA-aware scheduling to ensure that a proper NUMA node is available for the pod scheduled to a node when a topology-aware scheduling policy is enabled in the kubelet.
The following figure shows the Volcano NUMA-aware scheduling process.
Figure 3 Scheduling process
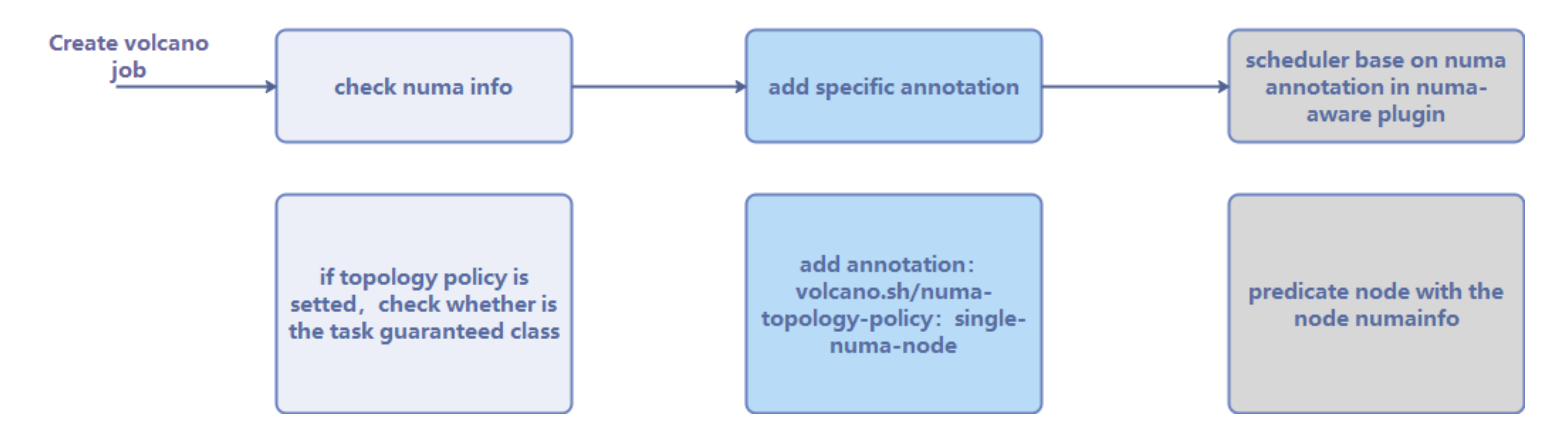
After a workload is created and Volcano is set as the scheduler, the system checks whether the configured topology policy is correct and then adds the topology policy to the annotations. Then, the NUMA-aware component determines whether the target node has available NUMA resources. Finally, the scheduler performs NUMA-aware scheduling based on the results provided by the NUMA-aware component and the topology policy in the annotations. For cross-NUMA scheduling, the scheduler follows a scoring principle:
Score = Weight x (100 – 100 x numaNodeNum/maxNumaNodeNum)
This ensures that pods are scheduled to the worker nodes that minimize the need to span across NUMA nodes.
Figure 4 Volcano scheduling
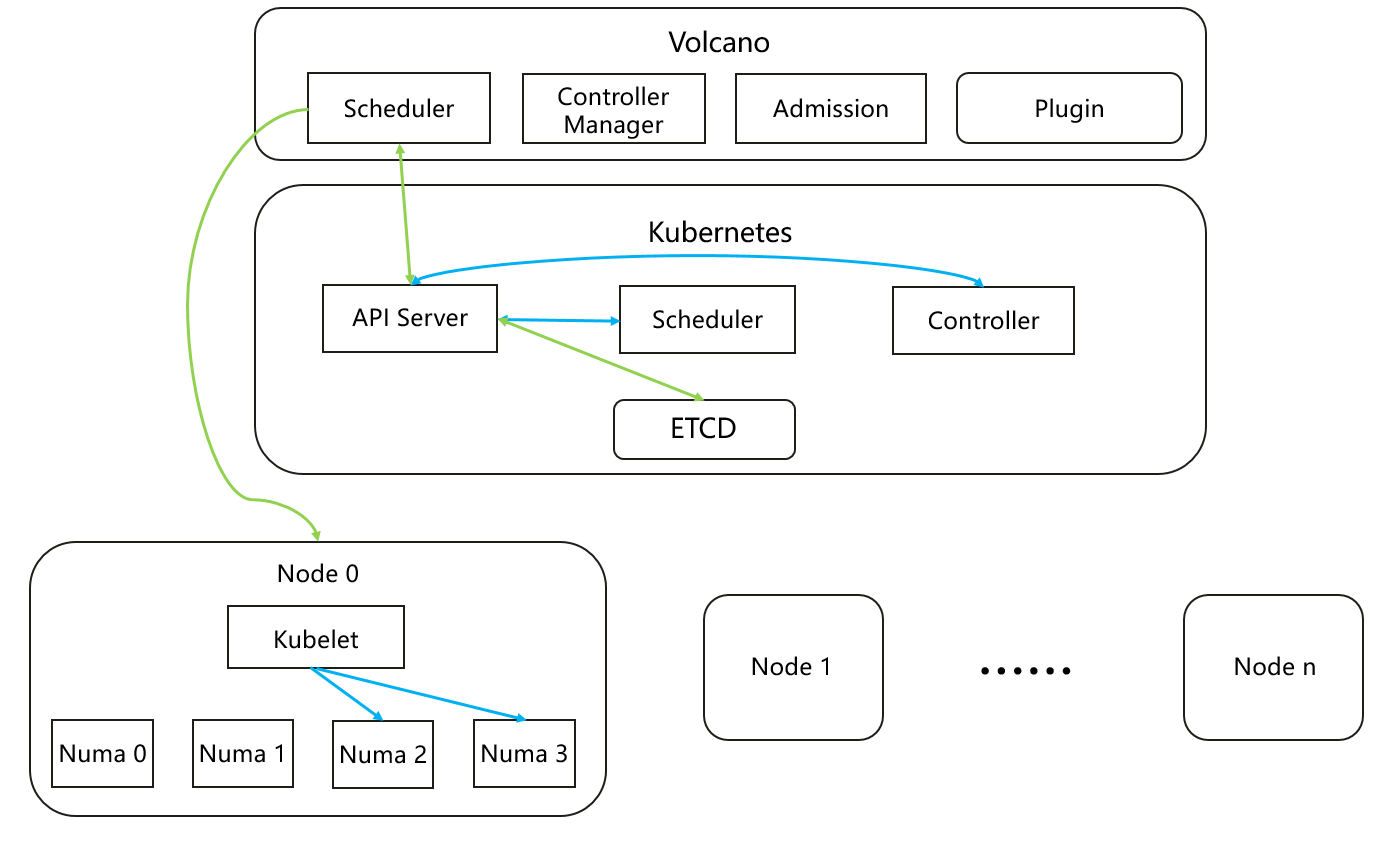
Volcano's scheduling policies work at the cluster level, ensuring workloads are scheduled to the most optimal nodes. However, resource allocation within a node, such as selecting specific NUMA resources for workloads, is handled by the kubelet, not Volcano. As a result, while workloads may be scheduled to an optimal node, they might not always be assigned the best NUMA resources within that node. Based on Volcano's cluster-level scheduling, this solution further optimizes NUMA resource allocation at the node level after a container is placed on a node.
Related Features
This feature depends on the resource management module and Prometheus. The resource management module provides APIs for viewing custom resource definitions (CRDs) and custom resources (CRs), and Prometheus provides the monitoring capability.
Instances
Code link: openFuyao/volcano-config-service (gitcode.com)
Installation
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes 1.21 or later has been deployed.
- Prometheus has been deployed.
- containerd 1.7 or later has been deployed.
Procedure
Deployment on the openFuyao Platform
- In the left navigation pane of the openFuyao platform, choose Application Market > Applications. The Applications page is displayed.
- Select Extension in the Type filter on the left to view all extensions. Alternatively, you can enter volcano in the search box to search for the component.
- Click the volcano-config-service card. The details page for the scheduling extension is displayed.
- Click Deploy. The Deploy page is displayed.
- Enter the application name and select the desired installation version and namespace.
- Enter the values to be deployed in Values.yaml.
- Click Deploy.
- In the left navigation pane, click Extension Management to manage the scheduling component.
NOTE
The deployment will modify the kubelet configuration items on the nodes, causing kubelet to restart. Proceed with caution in production environments.
Standalone Deployment
In addition to installation and deployment through the application market, this component also supports standalone deployment. The procedure is as follows:
-
Pull the image.
helm pull oci://harbor.openfuyao.com/openfuyao-catalog/charts/volcano-config-service --version xxxReplace xxx with the version of the Helm image to be pulled, for example, 0.0.0-latest.
-
Decompress the installation package.
tar -zxvf volcano-config-service-xxx.tgz -
Disable openFuyao and OAuth.
vim volcano-config-service/charts/volcano-config-website/values.yamlSet the enableOAuth and openFuyao options to false.
-
Install the component.
helm install volcano-config-service ./ -
Integrate with Prometheus.
For details, see Task Scenario 2 and Task Scenario 3 in the NUMA-aware Scheduling Development Guide.
-
Access the standalone frontend.
You can access the standalone frontend by visiting http://client login IP address of the management plane:30881.
Viewing the Overview Page
In the left navigation pane of the openFuyao platform, choose Computing Power Optimization Center > NUMA-aware Scheduling > Overview. The Overview page is displayed.
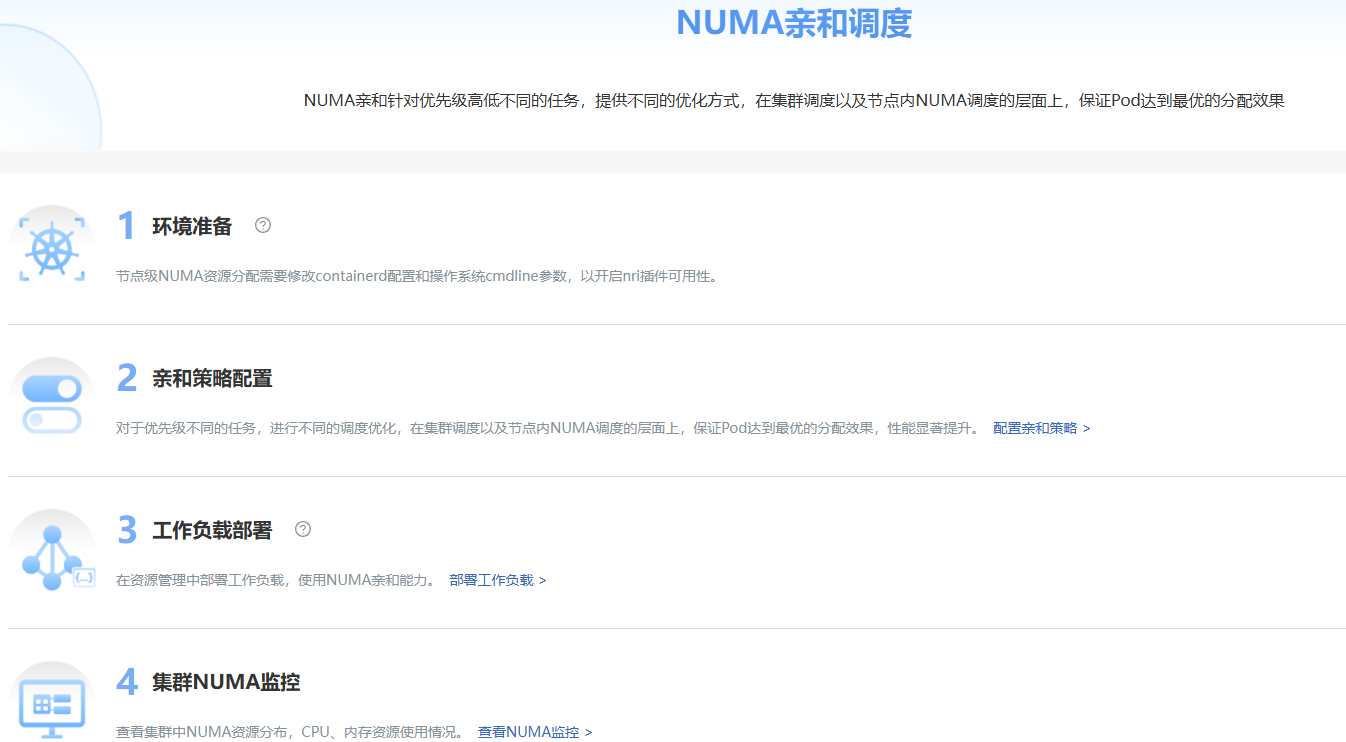
This page displays the NUMA-aware scheduling workflow.
Figure 5 Overview
Prerequisites
The volcano-config-service extension has been deployed in the application market.
Context
On this page, you can view the NUMA-aware scheduling workflow, including environment preparation, affinity policy configuration, workload deployment, and monitoring of NUMA resources in a cluster.
Restrictions
None.
Procedure
Choose NUMA-aware Scheduling > Overview. The Overview page is displayed.
- In the Environment Preparation step, you can modify Kubernetes configurations required for node-level NUMA resource allocation to enable the node topology policy and optimal distance switches. You can click
to view the configuration method.
- In the Affinity Policy Configuration step, you can click Configure Affinity Policy next to the description to go to the affinity policy configuration page.
- In the Workload Deployment step, you can use the workload deployment function to schedule workloads. You can click Deploy Workloads to go to the workload deployment page.
- In the Cluster NUMA Monitoring step, information about NUMA resources in clusters is displayed. You can click Go to NUMA Monitoring to go to the page.
Configurations on the Affinity Policy Configuration Page
In the left navigation pane of the openFuyao platform, choose Computing Power Optimization Center > NUMA-aware Scheduling > Affinity Policy Configuration. The Affinity Policy Configuration page is displayed.
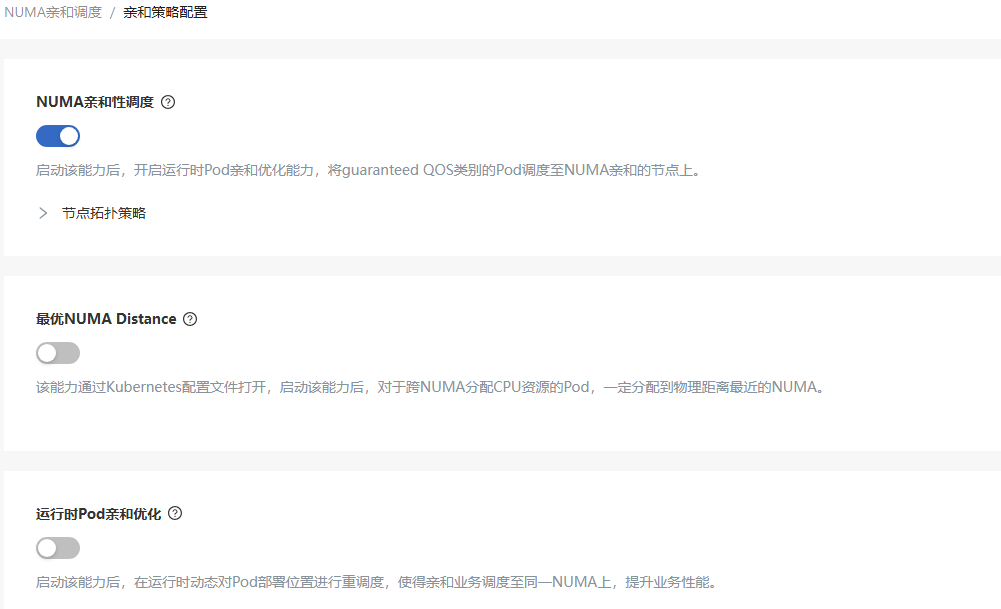
Figure 6 Affinity Policy Configuration
Configuring an Affinity Policy
Prerequisites
You must have the platform admin or cluster admin role.
Context
You need to modify the scheduling policies of a scheduling extension already deployed.
Restrictions
The scheduling extension that supports scheduling policy configuration has been deployed.
Procedure
-
In the left navigation pane of the openFuyao platform, choose Computing Power Optimization Center > NUMA-aware Scheduling > Affinity Policy Configuration. The Affinity Policy Configuration page is displayed. On this page, you can view the scheduling policy configurations.
-
Click the switch of each scheduling policy to enable or disable the scheduling policy. Click
next to a scheduling policy to view its details.
Using the Cluster-Level NUMA Monitoring Page
In the left navigation pane of the openFuyao platform, choose Computing Power Optimization Center > NUMA-aware Scheduling > Cluster NUMA Monitoring. The Cluster NUMA Monitoring page is displayed.
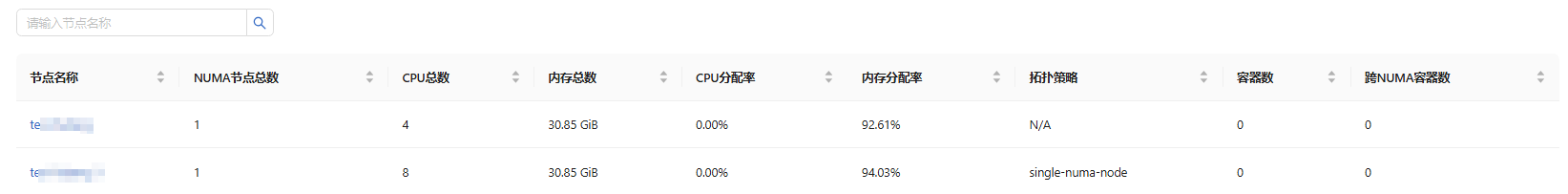
This page displays the total NUMA nodes, the total CPUs, total memory, CPU allocation rate, memory allocation rate, topology policy, the number of containers, and the number of cross-NUMA containers of all nodes in the cluster.
Figure 7 Cluster NUMA monitoring
Viewing NUMA Resource Information
Prerequisites
The volcano-config-service extension has been deployed in the application market.
Context
This page enables you to view the information about a specific NUMA node, including the CPU and memory resources, to learn about the NUMA allocation of the node.
Restrictions
This feature is supported only for nodes with a NUMA architecture. NUMA resource information is retrieved using the numactl command.
Procedure
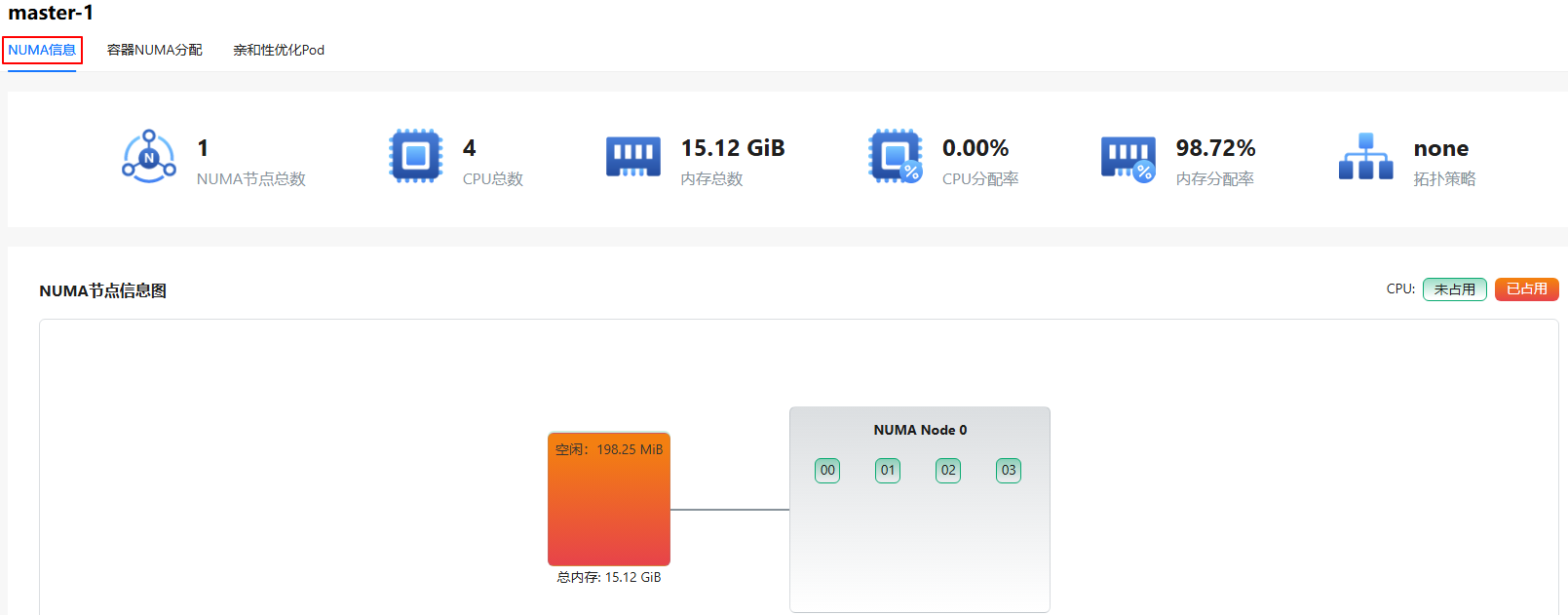
Click a node in the Node name column. The NUMA Information page is displayed.
- This page displays the total NUMA nodes, total CPUs, total memory, CPU allocation rate, memory allocation rate, topology policy, and node NUMA topology.
- The node NUMA topology displays the CPU IDs of each NUMA node. Red indicates that the CPU is occupied, and green indicates that the CPU is not occupied. Each NUMA node has a local memory. Light green indicates that the memory is idle, and red indicates that the memory is occupied.
- The NUMA-Distance table shows the access latency between a NUMA node and the local memory of any node. Higher values indicate higher latency during actual use.
Figure 8 Information about NUMA resources on a node
Viewing Information About NUMA Allocation in Container
Prerequisites
The volcano-config-service extension has been deployed in the application market.
Context
This feature enables you to view the detailed information about NUMA resource allocation for a container.
Restrictions
This feature is supported only for nodes with a NUMA architecture.
Procedure
- Click a node in the Node name column.
- Click the NUMA Allocation in Container tab.
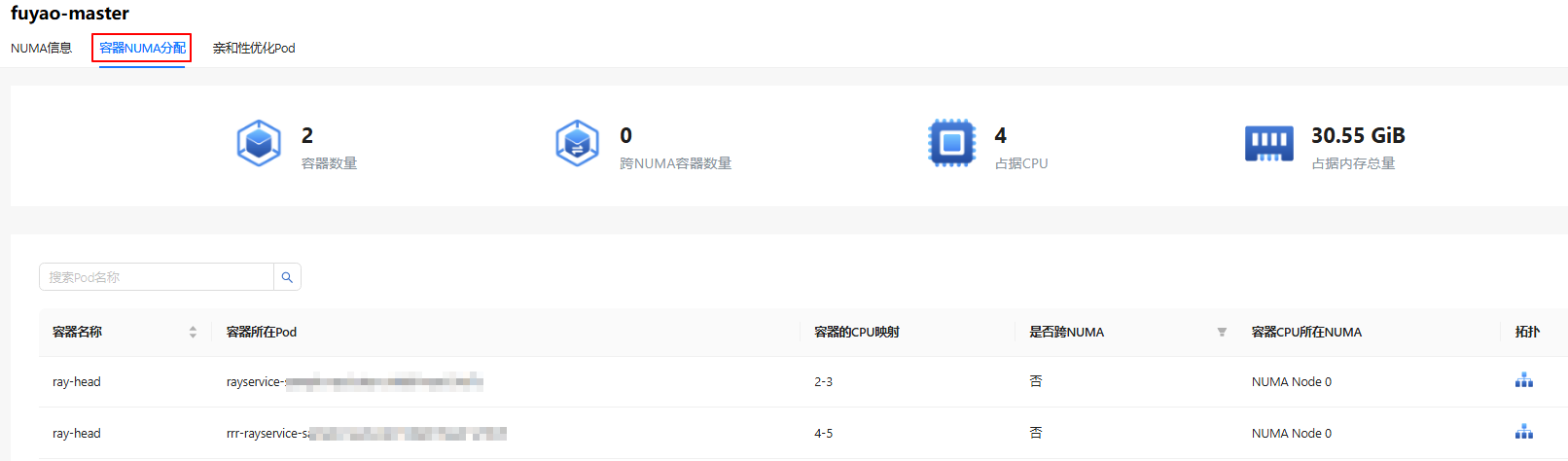
- This tab displays the overview data, such as the number of containers, the number of cross-NUMA containers, used CPU, and total memory usage.
- The table displays the container name, pod of container, container CPU mapping, cross-NUMA node, NUMA node of container CPU, and topology. You can also search for pods by pod name.
- Click
in the Topology column to view the container topology. For details about the topology, see Topology Description.
Figure 9 NUMA allocation in container
Viewing a Pod Whose Placement Is Optimized Based on Affinity
Prerequisites
The volcano-config-service extension has been deployed in the application market.
Context
This feature enables you to check the scheduling of a pod whose placement is optimized based on affinity.
Restrictions
Only NUMA nodes with the Arm architecture are supported. The OS is openEuler 22.03 LTS SP4. Pods that do not exclusively occupy resources and have network affinity are scheduled to the same NUMA node.
Procedure
- Click a node in the Node name column.
- Click the Affinity-optimized Pod tab.
- The table displays the number of affinity pods and network affinity pod names in each NUMA of the node.
Figure 10 Affinity-optimized pod