AI Inference Hermes Routing
Feature Overview
hermes-router is a Kubernetes (K8s)-native AI inference intelligent routing solution. It is used to receive inference requests from users and forward the requests to the appropriate inference service backend. By maintaining a global view of KV-cache utilization and supporting Prefill–Decode (PD) disaggregation, it boosts inference efficiency, raises resource utilization, and hardens service stability. hermes-router applies to AI inference optimization in cloud native scenarios.
Application Scenarios
- This feature is deployed in the traditional aggregation inference architecture and supports intelligent forwarding of inference requests.
- This feature is deployed in a static xPyD inference architecture and supports intelligent forwarding of inference requests in the PD disaggregation scenario.
Supported Capabilities
- Implements an intelligent routing architecture oriented to the K8s environment and handles user requests in an end-to-end manner.
- Allows users to configure the backend architecture and routing policy of routes.
- Supports deployment in the K8s environment using Helm charts.
Highlights
- Module decoupling: Modules such as configuration loading, service discovery, indicator collection, and routing policy are decoupled. The functions can be combined and are easy to maintain.
- Extensibility: The factory and policy modes are used to enable iterative updates of routing policies while adhering to the open closed principle.
- Intelligent routing: The optimal backend is selected based on the KV cache matching degree and backend load, improving inference efficiency.
Implementation Principles
The runtime sequence diagram of the feature is shown below:
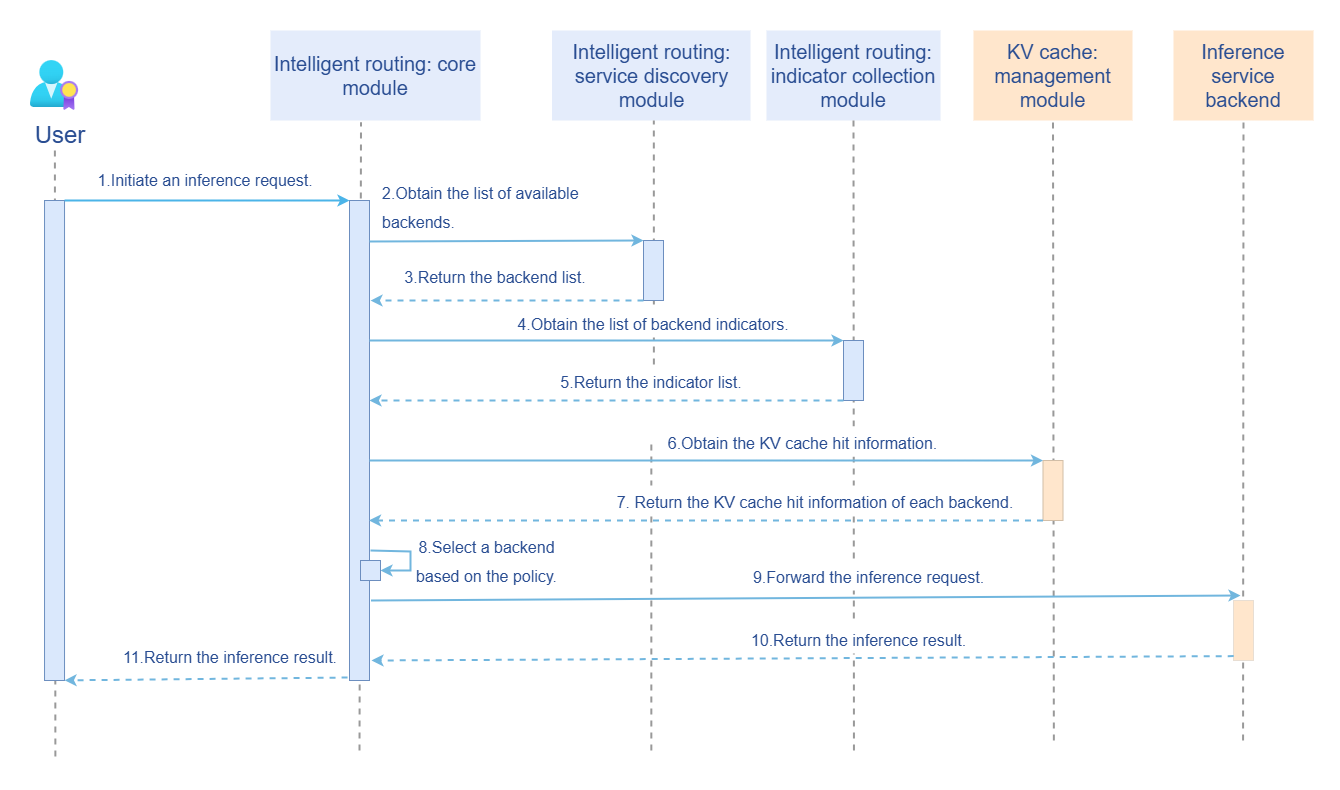
The sequence diagram begins when a user issues an inference request. Before this, intelligent routing has been initialized. Therefore, the initialization phase is described first.
- Configure the intelligent routing reading.
- Start the service discovery module (periodically updating the backend list).
- Start the indicator collection module (periodically updating the backend load indicator).
The process of handling an inference request is as follows:
- Receive the inference request from the user.
- Call the service discovery module to obtain the available backend list.
- Call the indicator collection module to obtain the backend load indicator.
- Call the KV cache management module to obtain the matching degree of each backend for the request.
- Select the optimal backend based on the routing policy and forward the request.
- Receive the backend inference result and return it to the user.
Relationship with Related Features
- This feature depends on inference engines, such as vLLM, to provide inference services and indicator interfaces.
- This feature depends on KV cache management tools, such as Mooncake, to provide global KV cache information.
Installation
Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements
hermes-router has no special requirements on the hardware environment.
Software Requirements
- Kubernetes v1.33.0 and later are used.
Starting the Installation
Using openFuyao Platform
- Log in to the openFuyao management plane.
- In the navigation pane, choose Application Market > Applications. The Applications page is displayed.
- Select AI/Machine learning in the Scenario area on the left and search for the hermes-router card. Alternatively, enter hermes-router in the search box.
- Click the hermes-router card to go to the Details page.
- Click Deploy. The Deploy page is displayed.
- Enter the application name and select the desired installation version and namespace. You can select an existing namespace or create a namespace. For details about how to create a namespace, see Namespace.
- Configure the route on the Values.yaml tab page of the Parameter Configuration area.
- Click Deploy to complete the installation.
Independent Deployment
In addition to the openFuyao platform-based installation and deployment, the independent deployment is also supported. The following two ways are provided if you use the independent deployment method:
- Obtain the project installation package from the official openFuyao image repository.
-
Obtain the project installation package.
helm pull oci://helm.openfuyao.cn/charts/hermes-router --version xxxReplace
xxxwith the actual project installation package version, for example,0.0.0-latest. The obtained installation package is a compressed package. -
Decompress the installation package.
tar -zxvf hermes-router -
Install and deploy the extension.
Run the following command in the directory where hermes-router is located:
helm install --generate-name ./hermes-router
- Perform the following operations on the openFuyao GitCode repository:
-
Obtain the project from the repository.
git clone https://gitcode.com/openFuyao/hermes-router.git -
Install and deploy the extension. Run the following command in the directory where hermes-router is located:
helm install --generate hermes-router/charts/hermes-router
Configuring AI inference routing
Prerequisites
- You have obtained the hermes-router project file.
- hermes-router has not been installed.
Context
None.
Constraints
- Currently, gateway capabilities such as request authentication are not supported. Do not expose the service entry to irrelevant users.
- Currently, only the vLLM inference engine is supported.
- Currently, only the AI inference scenario is supported. The AI training scenario is not supported.
Procedure
-
Prepare the values.yaml configuration file.
Ensure that you have obtained the Helm chart folder of the hermes-router project and found the values.yaml configuration file. The
appconfiguration segment in the file defines the core parameters for AI inference routing. -
Set basic routing parameters.
- app.namespace: Kubernetes namespace associated with the routing service, which is used to limit the scope of operations such as service discovery. For example,
namespace: "ai-inference". - app.strategy: specifies the routing policy. The KV cache aware policy and polling policy are supported. For example,
strategy: "kv-aware". - app.timeout: timeout interval (in seconds) of non-streaming responses. If a request is not completed within the timeout interval, the request is terminated. For example,
timeout: 120.
- app.namespace: Kubernetes namespace associated with the routing service, which is used to limit the scope of operations such as service discovery. For example,
-
Configure service discovery rules.
Use app.discovery to configure the automatic discovery mechanism of the backend inference service.
- app.discovery.type: service discovery type. Currently, only k8s-service (service discovery based on native K8s deployment) is supported.
- app.discovery.interval: service discovery refresh interval (in seconds). The backend service list is periodically updated. For example,
interval: 5interval: 5. - app.discovery.labelSelector: filters backend services based on K8s labels. Only services with the specified labels will be matched. For example,
labelSelector: { app: vllm }. - app.discovery.inferencePort: port of the backend inference service. For example,
inferencePort: 8000. - app.discovery.timeout: timeout interval of the service discovery operation (in seconds). For example,
timeout: 10.
-
Configure indicator collection parameters.
Set backend service indicator collection rules in app.collector to support the KV cache aware policy.
- app.collector.type: indicator collection type. Currently, only vllm is supported.
- app.collector.interval: indicator refresh interval (in seconds). Backend service indicators are periodically collected. For example,
interval: 5. - app.collector.timeout: indicator collection timeout interval (in seconds). For example,
timeout: 10. - app.collector.metrics: list of indicators to be collected, for example, XPU cache usage
vllm:gpu_cache_usage_perc.
-
Configure the information about the KV cache global manager.
If the KV cache aware policy is used, you need to configure the connection parameters for the KV cache global manager using app.kvmanager.
- app.kvmanager.url: URL for accessing the KV cache global manager, for example,
url: "http://10.96.xxx.xxx". - app.kvmanager.port: port of the KV cache global manager, for example,
port: 8080. - app.kvmanager.matchPath: route matching interface path for the KV cache global manager, for example,
matchPath: "/match_sort". - app.kvmanager.timeout: timeout interval (in seconds) for accessing the KV cache global manager, for example,
timeout: 10.
- app.kvmanager.url: URL for accessing the KV cache global manager, for example,
-
Deploy the route to apply the configurations.
Users can deploy the route to apply the configurations by referring to Installation.
Related Operations
After installation and deployment, users can update the AI inference routing configurations by modifying either the ConfigMap or the values.yaml file.
Using the AI inference service
Prerequisites
- The hermes-router AI inference service has been deployed.
- The inference backend in aggregation or PD disaggregation mode has been successfully deployed, and hermes-router is able to correctly discover backend services and inference indicators.
- You have obtained the entry URL of hermes-router, for example,
http://localhost:8000/rest/hermes-router/v1beta1/v1/chat/completons.
Context
- The inference request API adopts the OpenAI API style.
- Streaming and non-streaming responses are supported.
Constraints
- Currently, only plain text inference of the OpenAI API style is supported. Multimodal inference is not supported.
Procedure
- Construct an inference request. The following is an example:
{
"model": "deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "*Introduce the openFuyao open-source community.*"}],
"stream": true
}
- Send an inference request to hermes-router. The following uses curl as an example:
curl http://localhost:8000/rest/hermes-router/v1beta1/v1/chat/completons \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "*Introduce the openFuyao open-source community.*"}],
"stream": true
}'
- Receive the inference result.
- Streaming responses return JSON objects in chunks, each starting with
data:. - Non-streaming responses return the complete result in a single batch.
Related Operations
None.