Integrated AI Inference Deployment
Feature Overview
Integrated AI inference deployment is an end-to-end integrated deployment solution designed for optimizing AI inference services in the cloud-native environment. Based on a Helm chart, this solution seamlessly integrates three core AI inference acceleration modules: the intelligent routing (hermes-router), high-performance inference backend (Inference Backend), and global KV cache management (cache-indexer) modules. This offers a complete deployment link for AI inference acceleration components, covering request access, inference execution, and resource management for a one-stop deployment experience.
Application Scenarios
- Deployment of the traditional aggregation inference architecture: The aggregation inference mode based on vLLM is supported, which applies to small- and medium-scale inference scenarios.
- Deployment of the prefill-decode (PD) disaggregation inference architecture: The xPyD high-performance inference architecture with the disaggregated prefill and decode phases is supported, which applies to large-scale inference scenarios.
Supported Capabilities
- The load balancing algorithm based on KV cache awareness, GPU cache usage, and request waiting queue length is used to implement end-to-end inference request scheduling.
- Users can configure the routing policies of intelligent routing.
- The inference engines of the aggregation mode and xPyD disaggregation mode are supported.
- Users can configure the PD disaggregation mode of the inference engines and the number of xPyD inference engine nodes.
- Distributed KV cache metadata management is supported, and the KV cache awareness capability of global inference nodes is provided.
- The inference acceleration of Huawei Ascend 910B4 chips is adapted.
- Users can configure inference chips.
- Inference clusters can be deployed in the Kubernetes (K8s) environment in one-click mode using Helm.
Highlights
- KV-aware routing policy: Compared with traditional load balancing, the KV-aware routing policy implements more intelligent request routing by sensing the KV cache status of global inference nodes, which reduces unnecessary repeated KV cache computing.
- PD disaggregation architecture: The industry-leading PD disaggregation architecture is supported, which greatly improves the inference throughput of foundation models.
- Integration of vLLM and Mooncake: The vLLM v1 architecture is integrated with the Mooncake distributed KV cache management system, which achieves high-speed KV cache transmission across instances.
- One-click deployment: Helm charts are used to implement one-click integrated deployment of the three components in the K8s environment.
Implementation Principles
PD Aggregation Mode
Figure 1 Integrated AI inference deployment in PD aggregation mode
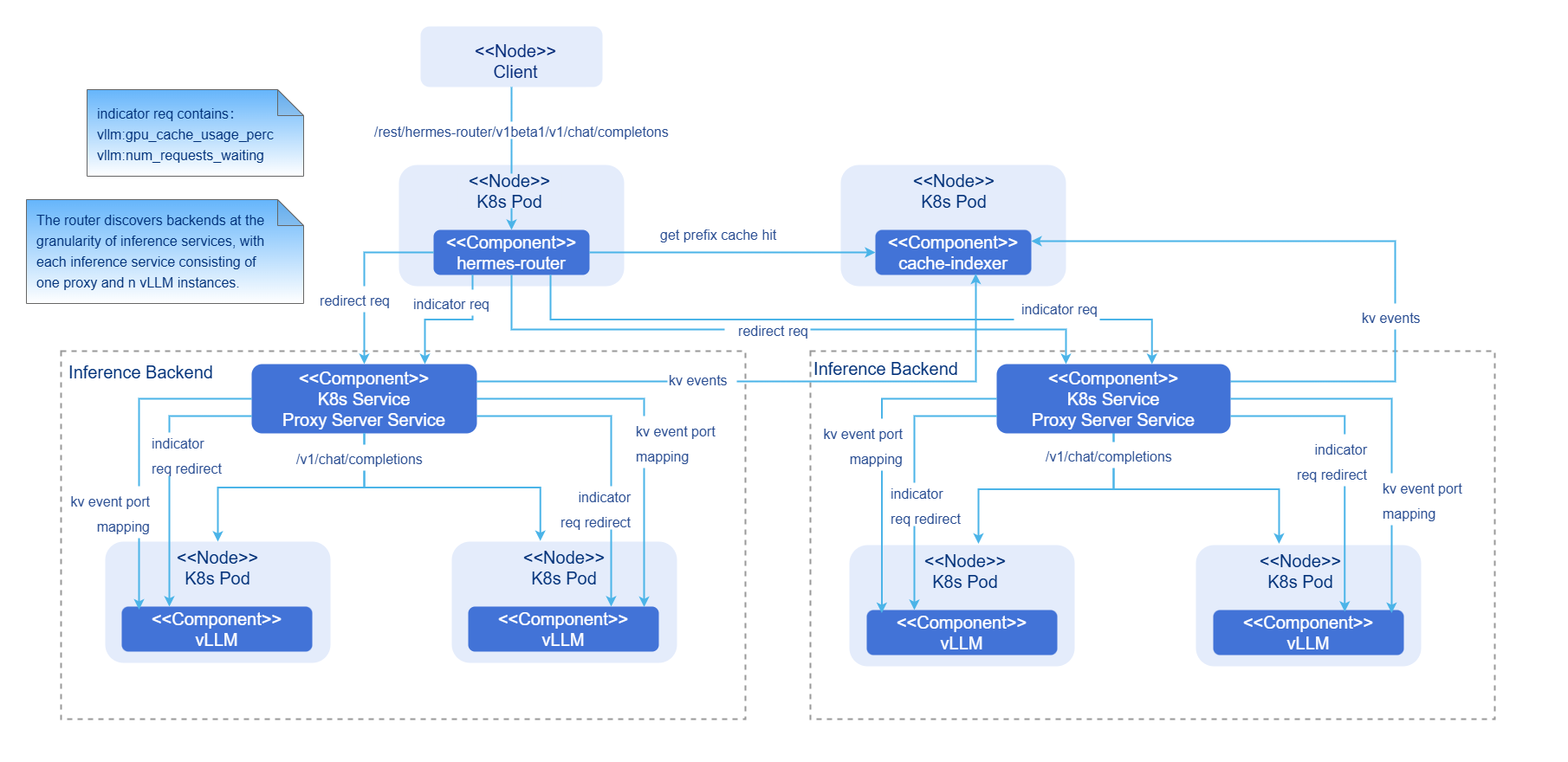
- hermes-router: intelligent routing module. It receives user requests and forwards the requests to the optimal inference backend service based on the routing policy.
- cache-indexer: global KV cache manager, which provides data support for routing decision-making.
- Inference Backend: inference backend module, which provides high-performance foundation model inference services based on vLLM. It consists of one proxy server service and n vLLM inference engine instances.
- Proxy Server Service: traffic entry of the inference backend service.
- vLLM: vLLM inference engine instance.
Component initialization process:
-
Intelligent routing:
- Configure the intelligent routing reading.
- Start the inference backend service discovery module (periodically updating the backend list).
- Start the inference backend indicator collection module (periodically updating the backend load indicator).
-
Inference backend:
- Start the vLLM inference engine instance based on the configuration.
- Bind the vLLM inference engine instance to a hardware device and load the model.
-
Global KV cache manager:
- Start the cache-indexer instance based on the configuration.
- Start the automatic discovery module (periodically updating the inference instance list) for the inference engine instance.
Request process:
- Request access: A user request reaches hermes-router first.
- KV cache query: hermes-router queries the prefix hit information of the request in the cluster from cache-indexer.
- Routing decision-making: The optimal inference backend service is selected based on the KV cache hit status and GPU usage.
- Request forwarding: The request is forwarded to the selected inference backend service.
- Inference execution: The vLLM inference engine executes the computing.
- Result return: The vLLM inference engine generates the request result and returns the result to hermes-router, and then returns the result to the client.
- Asynchronous update of global KV cache management: The prefill inference engine generates KV events during prefilling. cache-indexer subscribes to the KV events and updates the global KV cache metadata in real time.
PD Disaggregation Mode
Figure 2 Integrated AI inference deployment in PD disaggregation mode
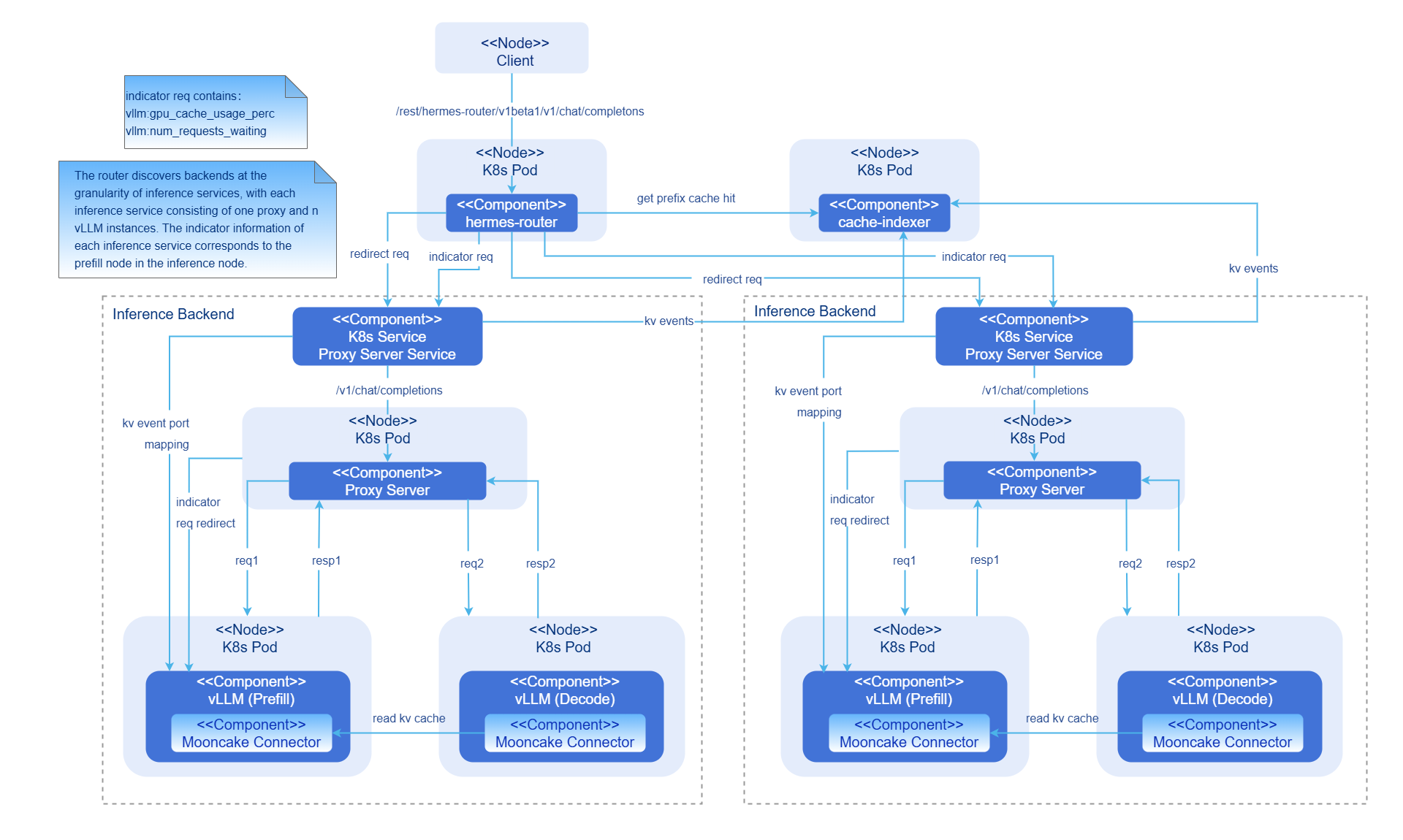
- hermes-router: intelligent routing module. It receives user requests and forwards the requests to the optimal inference backend service based on the routing policy.
- cache-indexer: global KV cache manager, which provides data support for routing decision-making.
- Inference Backend: inference backend module, which provides high-performance foundation model inference services based on vLLM. It consists of one proxy server service, one proxy server instance, n vLLM prefill inference engine instances, and n vLLM decode inference engine instances.
- Proxy Server Service: traffic entry of the inference backend service.
- Proxy Server: Layer 2 routing forwarding component. It is responsible for load balancing routing in each inference backend service.
- vLLM: vLLM inference engine instance.
- Mooncake Connector: high-speed KV cache P2P transmission between PD instances.
Component initialization process:
-
Intelligent routing:
- Configure the intelligent routing reading.
- Start the inference backend service discovery module (periodically updating the backend list).
- Start the inference backend indicator collection module (periodically updating the backend load indicator).
-
Inference backend:
- Start the vLLM inference engine instance based on the configuration.
- Bind the vLLM inference engine instance to a hardware device and load the model.
- The prefill inference engine instance and the decode inference engine instance establish connections with the KV connector ports exposed by each other.
- Start the proxy server component and initiate automatic discovery of the inference engine instance (periodically updating the inference engine instance list).
-
Global KV cache manager:
- Start the cache-indexer instance based on the configuration.
- Start the automatic discovery module (periodically updating the inference instance list) for the inference engine instance.
Request process:
- Request access: A user request reaches hermes-router first.
- KV cache query: The router queries the prefix hit information of the request in the cluster from cache-indexer.
- Routing decision-making: The optimal inference backend service is selected based on the KV cache hit status and GPU usage.
- Request forwarding: The request is forwarded to the selected inference backend service.
- Layer-2 routing: The proxy server in the inference backend service forwards the inference request to the prefill inference engine with the lightest load based on the load balancing policy.
- Prefill execution: The prefill inference engine performs the computing and returns the result to the proxy server. The prefill inference engine updates the KV cache status and sends a KV event.
- Decoding execution: The proxy server forwards the request to the decode inference engine with the lightest load based on the load balancing policy. The decode inference engine connects to the prefill inference engine and starts decoding.
- Result return: The decode inference engine generates the request result and returns the result to the proxy server, and then the proxy server returns the result to the client through a router.
- Asynchronous update of global KV cache management: The prefill inference engine generates KV events during prefilling. cache-indexer subscribes to the KV events and updates the global KV cache metadata in real time.
Relationship with Related Features
- The intelligent routing component hermes-router depends on the inference engine (such as vLLM) to provide the inference service and indicator interface.
- The global KV cache manager cache-indexer depends on the inference engine (such as vLLM) to provide KV cache storage and removal events.
Related Instances
Example: values.yaml
Installation
Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements
- Each inference node has at least one inference chip.
- Each inference node has at least 16 GB memory and four CPU cores.
Software Requirements
- Kubernetes v1.33.0 or later is used.
Network Requirements
- You can access the image repository at oci://cr.openfuyao.cn.
Permission Requirements
- You have the permission to create RBAC resources.
Starting the Installation
Independent Deployment
This feature can be independently deployed in either of the following ways:
- Obtain the project installation package from the official openFuyao image repository.
-
Obtain the project installation package.
helm pull oci://cr.openfuyao.cn/charts/ai-inference-integration:*xxx*Replace
xxxwith the actual project installation package version, for example,0.0.0-latest. The obtained installation package is a compressed package. -
Decompress the installation package.
tar -xzvf ai-inference-integration -
Perform installation and deployment.
Assume that the release name is
a3iand the namespace isai-inference. Run the following command in the directory where the ai-inference-integration directory is located:helm install -n ai-inference a3i ./ai-inference-integration
- Perform the following operations on the openFuyao GitCode repository:
-
Obtain the project from the repository.
git clone https://gitcode.com/openFuyao/ai-inference-integration.git -
Perform installation and deployment.
Assume that the release name is
a3iand the namespace isai-inference. Run the following command in the directory where the ai-inference-integration directory is located:cd ai-inference-integration/charts/ai-inference-integration
helm dependency build
helm install -n ai-inference a3i .
Configuring Integrated AI Inference Deployment
Prerequisites
- You have obtained the ai-inference-integration project file.
- The following components of ai-inference-integration are not installed and deployed: hermes-router, Inference Backend, and cache-indexer.
Procedure
-
Prepare the
values.yamlconfiguration file.Find the
values.yamlconfiguration file by referring to Starting the Installation. -
Configure the intelligent routing parameters.
Configure a routing policy.
- hermes-router.app.strategy: routing policy configuration. The KV cache aware policy and polling policy are supported. If you configure the
kv-awarepolicy, configurehermes-router.app.collector.kvmanagerand enable thecache-indexercomponent.
Configure the backend service discovery of the route.
- hermes-router.app.discovery.labelSelector.app: K8s service resource label for automatic service discovery of the inference backend. This label is configured in
inference-backend.service.label. For example, if the resource label of the inference backend K8s service is set tovllm, set the property toapp:vllm. - hermes-router.app.discovery.interval: automatic service discovery interval (unit: second) of the inference backend.
Configure the indicator discovery of the backend inference service of the route.
- hermes-router.app.collector.type: indicator collection type. Currently, only
vllmis supported. - hermes-router.app.collector.interval: indicator update interval (unit: second), which is used to periodically collect backend service indicators.
- hermes-router.app.collector.timeout: indicator collection timeout interval (unit: second).
- hermes-router.app.collector.metrics: list of indicators to be collected. For example, GPU cache usage
vllm:gpu_cache_usage_perc.
Configure the cache-indexer component discovery of the route.
- hermes-router.app.collector.kvmanager.url: service URL of the global KV cache manager. In K8s, the service name can be used to replace the IP address, for example,
url:"http://cache-index-service". The service name of the global KV cache manager can be configured incache-indexer.service.name. - hermes-router.app.collector.kvmanager.port: port of the global KV cache manager. The port of the global KV cache manager can be configured in
cache-indexer.service.port. - hermes-router.app.collector.kvmanager.matchPath: KV Aware interface of the global KV cache manager.
- hermes-router.app.collector.kvmanager.timeout: timeout interval (unit: second) for accessing the global KV cache manager.
Configure routing image pulling.
- hermes-router.image.repository: intelligent routing image address.
- hermes-router.image.tag: intelligent routing image tag.
- hermes-router.image.pullPolicy: intelligent routing image pulling policy.
- hermes-router.app.strategy: routing policy configuration. The KV cache aware policy and polling policy are supported. If you configure the
-
Configure the inference backend parameters.
Configure the basic switches of the inference backend.
- inference-backend.replicaCount: number of inference backend services. Each inference backend service contains multiple inference engine instances.
- inference-backend.isPDAggregated: whether the inference engine uses the PD disaggregation architecture. Currently, only the PD aggregation or PD disaggregation architecture is supported. Hybrid deployment is not supported.
Configure the inference backend model.
- inference-backend.app.model: model address used by the inference engine.
Configure the K8s service of the inference backend.
- inference-backend.service.label: label of the K8s service resource of each inference backend.
Configure the inference engine in aggregation mode.
- inference-backend.app.aggregated.replicaAmount: number of inference engine instances in each inference backend service.
- inference-backend.app.aggregated.vllmBasePort: HTTP API port of an inference engine instance.
- inference-backend.app.aggregated.tensorParallelism: tensor parallelism size of an inference engine instance.
- inference-backend.app.aggregated.dataParallelism: data parallelism size of an inference engine instance.
Configure the inference engine in PD disaggregation mode.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.kvConnector: name of the KV connector used by the inference engine.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.kvConnectorModulePath: path of the KV connector package used by the inference engine.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.proxyServer.basePort: HTTP API port of the Layer 2 routing service in each inference backend service.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.proxyServer.discovery.interval: automatic service discovery interval (unit: second) of the inference engine.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.prefill.replicaAmount: number of the prefill inference engine instances in each inference backend service.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.prefill.vllmBasePort: HTTP API port of a prefill inference engine instance.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.prefill.connectorBasePort: KV cache connector communication port of a prefill inference engine instance.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.prefill.tensorParallelism: tensor parallelism size of a prefill inference engine instance.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.prefill.dataParallelism: data parallelism size of a prefill inference engine instance.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.decode.replicaAmount: number of the decode inference engine instances in each inference backend service.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.decode.vllmBasePort: HTTP API port of a decode inference engine instance.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.decode.connectorBasePort: KV cache connector communication port of a decode inference engine instance.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.decode.tensorParallelism: tensor parallelism size of a decode inference engine instance.
- inference-backend.app.disaggregated.decode.dataParallelism: data parallelism size of a decode inference engine instance.
Configure the inference engine resources in aggregation mode.
- inference-backend.resources.aggregated.limits.deviceName: AI inference chip name in the K8s resource limit of the inference engine. The number of used chips is
dataParallelism × tensorParallelism. For example, the name can be as follows:deviceName: "huawei.com/Ascend910". - inference-backend.resources.aggregated.requests.deviceName: AI inference chip name of the requested K8s resource of the inference engine. For example, the name can be as follows:
deviceName: "huawei.com/Ascend910".
Configure the inference engine in PD disaggregation mode.
- inference-backend.resources.disaggregated.prefill.limits.deviceName: AI inference chip name in the K8s resource limit of the prefill inference engine. For example, the name can be as follows:
deviceName: "huawei.com/Ascend910". - inference-backend.resources.disaggregated.prefill.requests.deviceName: AI inference chip name of the requested K8s resource of the prefill inference engine. For example, the name can be as follows:
deviceName: "huawei.com/Ascend910". - inference-backend.resources.disaggregated.decode.limits.deviceName: AI inference chip name in the K8s resource limit of the decode inference engine. For example, the name can be as follows:
deviceName: "huawei.com/Ascend910". - inference-backend.resources.disaggregated.decode.requests.deviceName: AI inference chip name of the requested K8s resource of the decode inference engine. For example, the name can be as follows:
deviceName: "huawei.com/Ascend910".
Configure inference backend image pulling.
- inference-backend.aggregated.image.repository: image address of the inference backend in aggregation mode.
- inference-backend.aggregated.image.tag: image tag of the inference backend in aggregation mode.
- inference-backend.aggregated.image.pullPolicy: image pulling policy of the inference backend in aggregation mode.
- inference-backend.disaggregated.image.repository: image address of the inference backend in disaggregation mode.
- inference-backend.disaggregated.image.tag: image tag of the inference backend in disaggregation mode.
- inference-backend.disaggregated.image.pullPolicy: image pulling policy of the inference backend in disaggregation mode.
-
Configure the parameters of the KV cache global manager.
Configure the inference backend service discovery of the global KV cache manager.
- cache-indexer.app.serviceDiscovery.labelSelector: K8s service resource label for automatic service discovery of the inference backend. This label is configured in
inference-backend.service.label. For example, if the resource label of the inference backend K8s service is set tovllm, set the property tolabelSelector: "app=vllm". - cache-indexer.app.serviceDiscovery.refreshInterval: automatic service discovery interval (unit: second) of the inference backend.
Configure the K8s service of the global KV cache manager.
- cache-indexer.service.name: name of the K8s service of cache-indexer.
- cache-indexer.service.port: K8s service port of cache-indexer.
Configure the image pulling of the global KV cache manager.
- cache-indexer.image.repository: cache-indexer image address.
- cache-indexer.image.tag: tag of the cache-indexer image.
- cache-indexer.image.pullPolicy: cache-indexer image pulling policy.
- cache-indexer.app.serviceDiscovery.labelSelector: K8s service resource label for automatic service discovery of the inference backend. This label is configured in
-
Configure applications.
Users can perform the deployment to apply the configurations by referring to Installation.
Using the AI Inference
Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements
- Each inference node has at least one inference chip.
- Each inference node has at least 16 GB memory and four CPU cores.
Software Requirements
- Kubernetes v1.33.0 or later is used.
- The following components of ai-inference-integration have been installed: hermes-router, inference-backend, and cache-indexer.
Network Requirements
- You can access the image repository at oci://cr.openfuyao.cn.
- When Huawei collective communication library (HCCL) high-speed communication across servers is used, RDMA devices are required.
Context
None
Constraints
- Currently, gateway capabilities such as request authentication are not supported. Do not expose the service entry to irrelevant users.
- Currently, only the vLLM inference engine is supported.
- Currently, only Mooncake P2P Connector is supported.
- Currently, the verification is supported only by the Ascend 910B4 inference chip.
- Currently, only the AI inference scenario is supported. The AI training scenario is not supported.
Procedure
-
Obtain the service access address.
1.1 Check the address for accessing the hermes-router service.
kubectl get svc -n ai-inference1.2 Record the IP address and port number of the hermes-router. The hermes-router service name is
[Helm installation name]-hermes-router. -
Send an inference request. (The curl command is used as an example for sending requests.)
2.1 Send a non-streaming inference request.
curl -X http://[Routing service IP address]:[Routing service port number]/rest/hermes-router/v1beta1/v1/chat/completons \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "Qwen/Qwen3-8B",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Introduce the openFuyao open-source community."}],
"stream": false
}'2.2 Send a streaming inference request.
curl -X http://[Routing service IP address]:[Routing service port number]/rest/hermes-router/v1beta1/v1/chat/completons \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "Qwen/Qwen3-8B",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Introduce the openFuyao open-source community."}],
"stream": true
}' -
Receive the inference result.
3.1 Non-streaming responses return the complete result in a single batch.
3.2 Streaming responses return JSON objects in chunks, each starting with
data:.
Related Operations
The release name a3i and namespace ai-inference are used as examples.
View the deployment status.
helm status a3i -n ai-inference
Update the configuration.
helm upgrade a3i ./charts/ai-inference-integration \
-n ai-inference \
-f custom-values.yaml
Uninstall the system.
helm uninstall a3i -n ai-inference
Export the configuration.
helm get values a3i -n ai-inference > current-values.yaml
Expand the inference instances.
helm upgrade a3i ./charts/ai-inference-integration \
-n ai-inference \
--set inference-backend.replicaCount=2
FAQ
-
Error information is reported on the hermes-router and proxy server during the initial phase.
Symptom: According to the Pod logs, many error requests are reported on the hermes-router and proxy server at the beginning.
Procedure: This is a normal phenomenon. After the hermes-router is initialized, it periodically sends the inference engine indicator query requests to the proxy server. The loading of the foundation model during the initialization of the inference engine instances takes a long time. As a result, the indicator query requests cannot be correctly responded. This issue does not occur after the inference engine instances are started.
-
The hermes-router and cache-indexer cannot discover inference services.
Symptom: An error is reported when hermes-router and cache-indexer automatically discover inference service instances based on the Pod logs.
Procedure: The service label selector may be incorrectly configured. The
hermes-router.app.discovery.labelSelector.appandcache-indexer.app.serviceDiscovery.labelSelectorproperties indicate the service discovery configurations of the hermes-router and cache-indexer for K8s service resources of the inference backend. The properties must be the same as theinference-backend.service.labelproperty.