PD Disaggregation
Feature Overview
Prefill-Decode Disaggregation (PD Disaggregation) is a KV cache-centric disaggregated decoding deployment mode. The prefill and decode phases are deployed in two independent clusters to fully utilize CPU, DRAM, and SSD resources to achieve tiered caching of the KV cache, which aims to maximize the throughput under latency-related service level objectives (SLOs), overcome performance bottlenecks in inference services, and demonstrate efficient performance in long-context input scenarios.
Application Scenarios
A KV cache-centric disaggregated inference framework is used to deploy the prefill and decode phases in independent clusters.
Supported Capabilities
PD Disaggregation makes full use of CPU, DRAM, and SSD resources to improve the throughput, demonstrating efficient performance in long-context input scenarios.
Highlights
-
Batch integration:
In the original serial queue, regardless of the prompt length in a request, the prefill node executes the request before taking the next one from the queue. In scenarios where the user input is short, if the serial execution mode is used, a large amount of NPU computing power is wasted. The queue consumption mechanism is integrated based on the user input length and actual load. For instance, requests shorter than 1,024 tokens are batched together by merging several small or existing batches to raise execution parallelism and boost overall throughput.
-
PD load awareness:
The absolute prefill length after prefix-cache hit is no greater than the preset threshold. On the one hand, if the prefill length of a request is short, the request can be effectively computed by adding the prefill request and the ongoing decoding request to the decoding engine. On the other hand, if the prefix cache hit is very long, prefill becomes memory-bound rather than compute-bound and can thus be computed more efficiently within the decoding engine. The number of remote prefill requests in the prefill queue is below the preset threshold. When the prefill queue is heavily backlogged, the prefill workers are lagging. In this case, it is better to perform the computing locally until more prefill workers are added.
Implementation Principles
PD Disaggregation adopts a KV cache-centric disaggregated inference framework. The prefill and decode phases are deployed in two independent clusters. Resources are allocated based on the specific requirements of each phase, ultimately achieving a balance between low latency and high throughput.
Relationship with Related Features
- Mooncake: As a communication tool in the PD disaggregation process, Mooncake can quickly transmit data such as the KV cache between the prefill and decode phases.
- vLLM: The vLLM can be used as an inference compute component in the prefill or decode phase in the PD disaggregation architecture to provide inference APIs.
Installation
Prerequisites
You need to check the mounting of shared storage and the network connectivity on the parameter plane. The details are as follows:
- Shared storage mounting
- Run the
ll /mntcommand to check whether the storage is automatically mounted. - If the storage is not mounted, run the
mount -t dpc /kdxf /mntcommand to mount the storage.
- Network connectivity on the parameter plane
-
Run the
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -link -g; donecommand to check the up or down status of the network port. If the network port is not down, the network port is normal. -
Run the
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -link_stat -g; donecommand to check whether the network port is intermittently disconnected. If the network port is not intermittently disconnected, the network port is normal. -
Run the
for i in {0..7};do hccn_tool -i $i -tls -g|grep "tls switch";donecommand to check the TLS configuration. The normal configuration is as follows: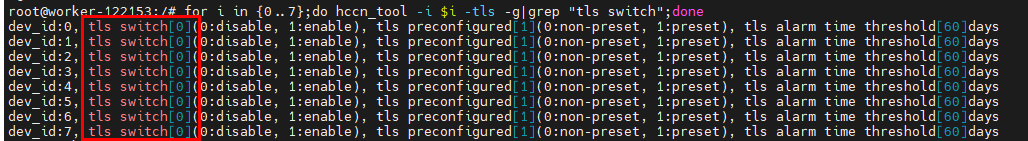
If the value is not 0, run the
for i in {0..7};do hccn_tool -i $i -tls -s enable 0;donecommand to set the TLS to 0. -
Run the following commands to disable the firewall:
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld -
To check the network connectivity on the parameter plane, use all cards in the cluster to ping the IP address of the same card.
5.1 Run the
cat /etc/hccn.confcommand on a server to record the value ofdevice ipin the cluster environment. The IP address is indicated by[ip]in the subsequent steps.5.2 Run the
for i in {0..7}; do hccn_tool -i $i -ping -g address [ip]; donecommand on all servers in use.5.3 Ensure that all IP addresses can be pinged, which indicates that the network connectivity on the parameter plane is normal.
Starting the Installation
-
Download the image.
Download the Ubuntu 22.04 image
mindie_dev-2.1.RC1.B152-800I-A2-py311-ubuntu22.04-aarch64.tar.gzand upload it to the server. -
Start the container.
2.1 Run the following command to go to the directory where the image is stored and load the image:
docker load -i mindie-XXX.tar.gz2.2 Run the following command to view the ID of the loaded image:
docker images2.3 Run the following command to start the container:
docker run --name openfuyao_pd -it -d --net=host --shm-size=500g \
--privileged=true \
-w /home \
--device=/dev/davinci_manager \
--device=/dev/hisi_hdc \
--device=/dev/devmm_svm \
--entrypoint=bash \
-v /mnt:/mnt \
-v /data:/data \
-v /dev:/dev \
-v /usr/local/Ascend/driver:/usr/local/Ascend/driver \
-v /usr/local/dcmi:/usr/local/dcmi \
-v /usr/local/bin/npu-smi:/usr/local/bin/npu-smi \
-v /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/sbin \
-v /home:/home \
-v /tmp:/tmp \
-v /opt:/opt \
-v /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai:/etc/localtime \
-v XXX \
bc6711a1ef08 #Use the image ID obtained earlier. -
Run a Git pull.
3.1 Run the following command to access the container:
docker exec -it openfuyao_pd bash #Replace **openfuyao_pd** with the actual container ID or container name. You can run the **docker ps** command to view the container information.3.2 Run the following commands to configure the proxy and run a Git pull:
# Network configuration
export http_proxy=http://[account]:[password]@proxyhk.huawei.com:8080
export https_proxy=http://[account]:[password]@proxyhk.huawei.com:8080
export no_proxy=127.0.0.1,localhost,local,.local
git config --global http.sslVerify false
# Mooncake downloading
git clone https://github.com/AscendTransport/Mooncake
# vLLM downloading
git clone https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm
# vllm-ascend downloading
git clone https://gitcode.com/openFuyao/vllm-ascend -
Install Mooncake.
Open the Mooncake/scripts/ascend/dependencies_ascend.sh script file in the pulled folder. Locate the following two lines of code for installing .whl packages, and comment them out to prevent repeated installation.
pip install mooncake-wheel/dist/*.whl --force
echo -e "Mooncake wheel pipinstall successfully."Run the installation script.
cd Mooncake/scripts/ascend
#Comment out the last two lines of code for installing .whl packages. If .whl packages are installed repeatedly, an error is reported.
bash dependencies_ascend.sh -
Install vLLM.
Run the following commands to go to the vllm directory and run the installation script:
cd vllm
VLLM_TARGET_DEVICE=empty pip install -v -e . -
Install vllm-ascend.
Go to the vllm-ascend directory, change the
torch-nupversion of therequirements.txtandpyproject.tomlfiles totorch-npu==2.7.1rc1, and run the following installation script:cd vllm-ascend/
#Modify the **requirements.txt** and **pyproject.toml** files.
COMPILE_CUSTOM_KERNELS=0 pip install -v -e ./Run the following command to check whether the installation is successful:
pip list | grep vllmIf the installation is successful, information similar to the following is displayed:
vllm 0.10.2rc2.dev7+g7c8271cd1.empty
vllm_ascend 0.1.dev789+g9b418ede4.d20250902 -
Install torch-npu.
Download the torch_npu package of the corresponding version
torch_npu-2.7.1.dev20250724-cp311-cp311-manylinux_2_28_aarch64.whland upload the package to the server.Run the following installation command in the corresponding directory:
pip install --no-index --no-deps --force-reinstall torch_npu**
Starting an Instance Using PD Disaggregation
Prerequisites
Mooncake, vLLM, and vllm-ascend have been installed in the container.
Context
PD Disaggregation deploys the prefill and decode phases in two independent clusters to fully utilize resources and improve the throughput.
Constraints
During the startup, the port used by each prefill instance must not conflict with that used by each decode instance, and the value of tp_size of the prefill instance must be greater than or equal to that of the decode instance.
Procedure
-
Start the prefill and decode phases separately.
1.1 Prepare the run_prefill.sh and run_decode.sh scripts. Replace
./Qwen3-8Bwith the actual model file path.run_prefill.sh
export HCCL_EXEC_TIMEOUT=204
export HCCL_CONNECT_TIMEOUT=120
export HCCL_IF_IP=0.0.0.0
export GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME="eth0"
export TP_SOCKET_IFNAME="eth0"
export HCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME="eth0"
export ASCEND_RT_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1
export VLLM_USE_V1=1
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/Ascend/ascend-toolkit/latest/python/site-packages:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
echo "HCCL_IF_IP=$HCCL_IF_IP"
vllm serve ./Qwen3-8B \
--host 0.0.0.0\
--port 8107 \
--tensor-parallel-size 2\
--seed 1024 \
--max-model-len 2000 \
--max-num-batched-tokens 2000 \
--trust-remote-code \
--enforce-eager \
--data-parallel-size 1 \
--data-parallel-address localhost \
--data-parallel-rpc-port 9100 \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.8 \
--kv-transfer-config \
'{"kv_connector": "MooncakeConnectorV1",
"kv_buffer_device": "npu",
"kv_role": "kv_producer",
"kv_parallel_size": 1,
"kv_port": "20001",
"engine_id": "0",
"kv_rank": 0,
"kv_connector_module_path": "vllm_ascend.distributed.mooncake_connector",
"kv_connector_extra_config": {
"prefill": {
"dp_size": 1,
"tp_size": 2
},
"decode": {
"dp_size": 1,
"tp_size": 2
}
}
}'run_decode.sh
export HCCL_EXEC_TIMEOUT=204
export HCCL_CONNECT_TIMEOUT=120
export HCCL_IF_IP=0.0.0.0
export GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME="eth0"
export TP_SOCKET_IFNAME="eth0"
export HCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME="eth0"
export ASCEND_RT_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2,3
export VLLM_USE_V1=1
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/Ascend/ascend-toolkit/latest/python/site-packages:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
echo "HCCL_IF_IP=$HCCL_IF_IP"
vllm serve ./Qwen3-8B \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 8207 \
--tensor-parallel-size 2\
--seed 1024 \
--max-model-len 2000 \
--max-num-batched-tokens 2000 \
--trust-remote-code \
--enforce-eager \
--data-parallel-size 1 \
--data-parallel-address localhost \
--data-parallel-rpc-port 9100 \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.8 \
--no-enable-prefix-caching \
--kv-transfer-config \
'{"kv_connector": "MooncakeConnectorV1",
"kv_buffer_device": "npu",
"kv_role": "kv_consumer",
"kv_parallel_size": 1,
"kv_port": "20002",
"engine_id": "1",
"kv_rank": 1,
"kv_connector_module_path": "vllm_ascend.distributed.mooncake_connector",
"kv_connector_extra_config": {
"prefill": {
"dp_size": 1,
"tp_size": 2
},
"decode": {
"dp_size": 1,
"tp_size": 2
}
}
}'1.2 Run the following commands to start the processes:
bash run_prefill.sh
bash run_decode.sh1.3 Create a port to start the service. Ensure that
prefiller-hosts,prefiller-ports,decoder-hosts, anddecoder-portscorrespond to the settings in the script.cd vllm-ascend/examples/disaggregated_prefill_v1/
python load_balance_proxy_server_example.py --host 0.0.0.0 --prefiller-hosts 127.0.0.1 --prefiller-ports 8107 --decoder-hosts 127.0.0.1 --decoder-ports 8207 --port 9090 -
Verify the service startup.
Create a port test. Replace
./Qwen3-8Bwith the actual model file path. The port for test access must be the same as that specified when the service is started (9090 in this example).curl -v -s http://127.0.0.1:9090/v1/completions -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"model": "./Qwen3-8B","prompt": "Hello. Who are you?","max_tokens": 256}'If an answer similar to the following is displayed, the configuration is successful.
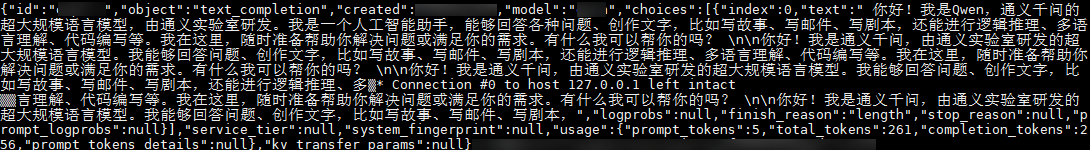
Follow-up Operations
-
To enable batch integration, add the following environment variable to the startup script of the prefill instance:
export BATCH_BY_REQUEST_LENGTH="true"Add the following parameter to the
vllm serveinstruction in the startup script of the prefill instance:--scheduling-policy "priority" -
To modify other configurations in the PD disaggregation instance, visit the following address: vllm-ascend/examples/disaggregated_prefill_v1/mooncake_connector_deployment_guide.md at main · vllm-project/vllm-ascend · GitHub.