KAE Operator
Feature Overview
Kubernetes provides access to special hardware resources (such as Kunpeng Accelerator Engine (KAE), NIC, InfiniBand adapter, and other devices) through device plugins. However, multiple software components (such as drivers, container runtimes, or other libraries) are required to configure and manage a node having these hardware resources. Installation of these components is complex, difficult, and error-prone. The KAE Operator uses the Operator Framework in Kubernetes to automatically manage all software components required for configuring KAE. These components include the KAE driver and KAE device plugin for Kubernetes.
KAE is a capability built into the Kunpeng 920 series processors. For details, see KAE Product Overview.
Applicable Scenarios
KAE-powered hardware acceleration: For services in the cluster that require KAE-powered hardware acceleration (such as encryption and decryption), the KAE Operator can automatically detect KAE-enabled nodes in the cluster and install and deploy necessary components.
Supported Capabilities
- Nodes with KAE devices can be automatically discovered.
- All necessary components of KAE can be automatically deployed and configured so that you can efficiently use KAE in Kubernetes clusters.
- When a device on a node is changed, components are automatically adjusted. For example, deployed services are reclaimed when a device goes offline.
Highlights
The KAE operator automatically manages all software components required for configuring the KAE, making KAE hardware easier to use and improving operational efficiency.
Implementation Principles
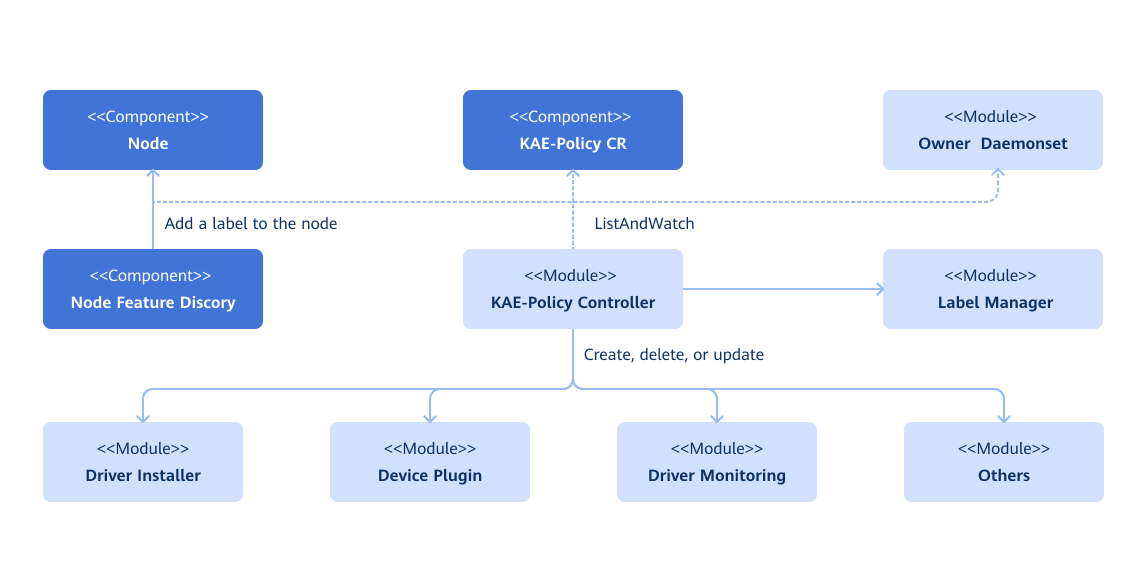
The operator observes changes in three types of resources:
- Custom resource definitions (CRDs) of the operator
- Nodes in the cluster (For example, a node is added to the cluster, or the label of a node in the cluster changes.)
- DaemonSets created by the operator
The operator manages two types of resources:
- Labels: The operator manages labels based on the system, kernel, and hardware devices discovered by the Node Feature Discovery (NFD) service, and assigns deployment-dependent labels to nodes.
- Components: The operator assembles resource files and installs services based on the CRD configuration.
The operator can manage components by:
- Installing or uninstalling components based on labels
- Upgrading or removing related components
Related Features
The KAE Operator currently manages the following components:
- KAE Driver Installer
- KAE Device Plugin
Figure 1 Implementation principles
Security Context for the Operator
Certain pods managed by the KAE Operator (for example, driver containers) require elevated privileges as follows:
privileged: truehostPID: truehostIPC: truehostNetwork: true
The reasons for elevating privileges are as follows:
- To access the file system and hardware devices of the host and install driver on the host
- To modify device permissions to enable usage by non-root users
Only Kubernetes cluster administrators need to access or manage the namespace to which the operator belongs. It is a good practice to establish appropriate security policies and prevent any other users from accessing the namespace to which the operator belongs.
Installation
Prerequisites
-
Ensure that kubectl and Helm CLI are installed on your host, or that a configurable application store or repository is available in the cluster.
-
To use the KAE driver container, all worker nodes or node groups running KAE workloads in a Kubernetes cluster must operate in the operating system (OS) of the same version (currently openEuler 22.03 LTS).
Worker node or node groups that run CPU workloads only may operate in any OS because the KAE Operator does not perform any configuration or management operation on a node that is not dedicated to KAE workloads.
-
The KAE node must be licensed. For details, see KAE Installation Preparations. In virtual machine (VM) scenarios, Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) and PCIe passthrough must be properly configured. For details, see Using KAE on a KVM.
-
Since driver installation depends on kernel packages such as
kernel-devel, each node must be configured with a Yum source of the correct version (matching the OS and version requirements).In an offline environment, you can configure the system image as the local image source. The following settings are for reference only. You need to adjust them based on the actual situation.
-
Download the OS image from the openEuler official website. Download the standard image (Offline Standard ISO) applicable to the server. Ensure that the downloaded image version matches the current system version. After downloading, upload the image file to a Linux environment, such as the
/mnt/isodirectory. -
Create a directory used for mounting the image.
mkdir -p /mnt/openEuler -
Mount the image to the
/mnt/openEulerdirectory.mount /mnt/iso/<OS image name eg: openEuler-22.03-LTS-x86_64-dvd.iso> /mnt/openEuler -
Configure the Yum source.
# Back up the existing Yum source
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/openEuler.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/openEuler.repo.bak
# Create the openEuler.repo file
cat << EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/openEuler.repo
[openEuler]
name=openEuler
baseurl=file:///mnt/openEuler
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///mnt/openEuler/RPM-GPG-KEY-openEuler
EOF -
Update the Yum source cache.
yum clean all
yum makecache
-
-
NFD is a dependency of the operator on each node. By default, the NFD master node and worker nodes are automatically deployed by the operator. If the NFD is already running in the cluster, its deployment must be disabled during operator installation.
values.yaml
nfd:
enabled: falseOne way to determine whether the NFD is running in the cluster is to check the NFD label on the node.
kubectl get nodes -o json | jq '.items[].metadata.labels | keys | any(startswith("feature.node.kubernetes.io"))'If the command output is
true, the NFD is already running in the cluster. In this case, configurenodefeaturerulesto install the custom KAE node discovery rules.nfd:
nodefeaturerules: true
Procedure
Deployment on the openFuyao Platform
Download the KAE Operator extension from the openFuyao application market and install it.
- Log in to the openFuyao platform. In the left navigation pane, choose Application Market > Applications.
- Search for kae operator in the application list and find the KAE Operator extension.
- Click the KAE Operator card. The application details page is displayed.
- On the details page, click Deploy in the upper-right corner. In the Installation Information area on the deployment page, set the application name, version information, and namespace.
- Click OK.
Common Scenarios
Procedure
-
Add the openFuyao Helm repository.
helm repo add openfuyao https://harbor.openfuyao.com/chartrepo/openfuyao-catalog \
&& helm repo update -
Install the KAE Operator.
-
Install the operator using the default configurations.
$ helm install --wait --generate-name \
-n kae-operator --create-namespace \
openfuyao/kae-operator -
Install the operator and specify the configuration options.
$ helm install --wait --generate-name \
-n kae-operator --create-namespace \
openfuyao/kae-operator \
--set <option-name>=<option-value>
-
If the operator is installed using the Helm application store or market, add the https://harbor.openfuyao.com/chartrepo/openfuyao-catalog repository and install it on the user interface (UI). For details, see Common Customization Options and Common Deployment Scenarios.
Common Customization Options
The following options are available when you use the Helm chart. These options can be used with --set when you install the operator using Helm.
The following table lists the most commonly used options. To view all options, run helm show values openfuyao/kae-operator. Table 1 Common options
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
nfd.enabled | Deploys the NFD service. If the NFD service is already running in the cluster, set this parameter to false.
| true |
nfd.nodefeaturerules | If this option is set to true, a CR containing a rule is installed. This rule enables NFD to discover KAE devices. | false |
node-feature-discovery.image.repository | Specifies the image path of the NFD service. | registry.k8s.io/nfd/node-feature-discovery |
node-feature-discovery.image.pullPolicy | Specifies the image pulling policy of the NFD service. | IfNotPresent |
node-feature-discovery.image.tag | Specifies the image version of the NFD service. | v0.16.4 |
operator.enabledHPRE | Enables high performance RSA engine (HPRE), which is a device management module of KAE. When this module is enabled, the HPRE device is managed. If the management of this device is not required in the cluster, set this parameter to false. | true |
operator.enabledSEC | Enables the KAE's SEC device management function. When this function is enabled, the SEC device is managed. If the management of this device is not required in the cluster, set this parameter to false. In the current version, the operator only manages HPRE device plug-ins. This field is reserved for future use. | false |
operator.enabledZIP | Enables the KAE's ZIP device management function. When this function is enabled, the ZIP device is managed. If the management of this device is not required in the cluster, set this parameter to false. In the current version, the operator only manages HPRE device plug-ins. This field is reserved for future use. | false |
operator.upgradeCRD | The operator upgrades CRDs using the pre-upgrade Helm hook. | false |
operator.cleanupCRD | The operator clears CRDs using the post-delete Helm hook. | false |
operator.image | Specifies the image path of the KAE Operator. | harbor.openfuyao.com/openfuyao/kae-operator |
operator.version | Specifies the image version of the KAE Operator. | latest |
operator.pullPolicy | Specifies the image pulling policy of the KAE Operator. | IfNotPresent |
daemonSets.labels | Specifies the custom label to be added to all pods managed by the KAE Operator. | {} |
daemonSets.tolerations | Specifies the custom tolerance to be added to all pods managed by the KAE Operator. | [] |
driver.enabled | By default, the operator deploys the KAE driver on the system as a container. When using the operator on a system where the driver is pre-installed, set this parameter to false. The operator will uninstall the installed Driver DaemonSet (if any).
| true |
driver.enabledCleanup | By default, uninstalling the operator or destroying the Driver DaemonSet does not uninstall the driver on the host machine. If you want to uninstall the driver on the host machine at the same time, set the value to true. | false |
driver.repository | Specifies the image repository of the driver. Specify another image repository if using a custom driver image. | harbor.openfuyao.com/openfuyao |
driver.image | Specifies the name of the driver image. If both driver.repository and driver.version are empty, set this field to the full image path. | kae-driver-installer |
driver.version | Specifies the driver version. | latest |
driver.env | Specifies the environment variables of the driver. Currently, the INSTALL_POLICY field is configurable. IfNotPresent: The existing driver on the node is not overwritten. Always: Uninstall the existing driver first, and then install the new one. | IfNotPresent |
devicePlugin.enabled | By default, the operator deploys the KAE device plug-in on the system. When using the operator on a system where the device plugin is pre-installed, set this parameter to false. The operator will uninstall the installed Device Plugin DaemonSet (if any).
| true |
devicePlugin.repository | Specifies the image repository of the device plug-in. Specify another image repository if using a custom driver image. | harbor.openfuyao.com/openfuyao |
devicePlugin.image | Specifies the image name of the device plug-in. If both driver.repository and driver.version are empty, set this field to the full image path. | kae-device-plugin |
devicePlugin.version | Specifies the device plug-in version. | latest |
psa.enabled | If the cluster uses Pod Security Admission (PSA) to restrict the behavior of pods, set this parameter to true. | false |
Common Deployment Scenarios
The following common deployment scenarios and example commands apply to hosts or VMs with KAE passthrough.
Specifying the Operator Namespace
The namespace to which the operator belongs is configurable and is specified during installation. For example, run the following command to install KAE Operator in the openfuyao namespace:
helm install --wait --generate-name \
-n openfuyao --create-namespace \
openfuyao/kae-operator
If no namespace is specified during the installation, all KAE Operator components are installed in the default namespace.
Preventing the KAE Driver from Being Installed on Certain Nodes
By default, the KAE Operator deploys the driver on all KAE worker nodes in the cluster. To prevent the driver from being installed on a certain KAE worker node, label the node as follows:
kubectl label nodes $NODE openfuyao.com/kae.deploy.driver=false
NOTE
- You are advised to apply this label before installing the KAE Operator.
- If the node is restarted or the device is uninstalled and you want to add it again, run this command again.
- If you need to install the driver on the node later, run the
kubectl label nodes $NODE openfuyao.com/kae.deploy.driver=truecommand.
Pre-Installing the KAE Driver
If the KAE driver has been installed on a KAE worker node, it does not need to be managed by the KAE Operator. In this case, run the following command:
helm install --wait --generate-name \
-n kae-operator --create-namespace \
openfuyao/kae-operator \
--set driver.enabled=false
Running a Custom Image
Specify the new image and repository by overwriting the default values in the helm install command. The following is an example:
helm install --wait --generate-name \
-n kae-operator --create-namespace \
openfuyao/kae-operator \
--set driver.repository=docker.io/your repository \
--set driver.version="0.1"
Upgrade
The KAE Operator supports dynamic updates to existing resources. This ensures that KAE policy settings in the cluster are always kept up to date.
Because Helm does not support automatic upgrades of existing CRDs, the KAE Operator Chart can be upgraded either manually or by enabling the Helm hook.
Upgrading CRDs Manually
-
Specify the operator release tag as an environment variable.
export RELEASE_TAG=v24.09 -
Update the CRDs for the KAE policy.
kubectl apply -f <path>/device.openfuyao.com_kaepolicies_crd.yamlOutput example
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kaepolicies.device.openfuyao.com configured -
Update the CRDs for the NFD.
kubectl apply -f <path>/nfd-api-crds.yamlOutput example
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/nodefeaturerules.nfd.k8s-sigs.io configured -
Update information related to the KAE Operator Chart.
helm repo update openfuyaoOutput example
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories...
...Successfully got an update from the "openfuyao" chart repository
Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈ -
Obtain values from the chart.
helm show values openfuyao/kae-operator --version=$RELEASE_TAG > values-$RELEASE_TAG.yaml -
Update the file as required.
-
Upgrade the operator.
helm upgrade kae-operator openfuyao/kae-operator -n kae-operator -f values-$RELEASE_TAG.yamlOutput example
Release "kae-operator" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: kae-operator
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu sep 1 15:05:52 2024
NAMESPACE: kae-operator
STATUS: kae-operator
REVISION: 2
TEST SUITE: None
Automatically Upgrading CRDs Using the Helm Hook
The KAE Operator supports automatic CRD upgrades using the pre-upgrade Helm hook. The operator.upgradeCRD parameter is used to control whether triggering this hook when the KAE Operator is upgraded using Helm. This function is disabled by default. To enable it, use the --set operator.upgradeCRD=true option when running the upgrade command.
-
Specify the operator release tag as an environment variable.
export RELEASE_TAG=v24.09 -
Update information related to the KAE Operator Chart.
helm repo update openfuyaoOutput example
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories...
...Successfully got an update from the "openfuyao" chart repository
Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈ -
Obtain values from the chart.
helm show values openfuyao/kae-operator --version=$RELEASE_TAG > values-$RELEASE_TAG.yaml -
Update the file as required.
-
Upgrade the operator.
helm upgrade kae-operator openfuyao/kae-operator -n kae-operator \
--set operator.upgradeCRD=true --disable-openapi-validation -f values-$RELEASE_TAG.yamlNOTE
- In this case, you need to set the
--disable-openapi-validationoption so that Helm does not attempt to verify whether the CR instances of the new chart are valid against the existing CRDs. The CR instances of the chart are valid for the upgraded CRDs. Therefore, compatibility is ensured. - Helm Hook uses the operator image. If the image cannot be pulled (possibly due to a network error), the hook will fail. In this case, uninstall the chart using the
--no-hooksoption to prevent the chart from being suspended due to hook failures during the uninstallation.
- In this case, you need to set the
Updating the CRs for the KAE Policy
The KAE Operator supports dynamic updates to custom resources of KAEPolicy through kubectl.
kubectl edit kaepolicy kae-policy
After the editing is complete, Kubernetes automatically updates the application to the cluster.
Uninstallation
To uninstall an operator, perform the following steps:
-
Remove the operator using the Helm CLI or through the openFuyao management plane:
helm delete -n kae-operator $(helm list -n kae-operator | grep kae-operator | awk '{print $1}') -
(Optional) List pods in the namespace to which the operator belongs to check whether the pods have been removed or are being removed.
kubectl get pods -n kae-operatorOutput example
No resources found.
By default, Helm does not remove existing CRDs when a chart is removed.
kubectl get crd kaepolicies.device.openfuyao.com
To solve this problem, the operator uses a post-delete Helm hook to clear up CRDs. The operator.cleanupCRD parameter controls whether this hook is enabled. By default, this parameter is disabled. You can enable this hook by specifying --set operator.cleanupCRD=true during installation or upgrades so that CRD cleanup is automatically performed when a chart is removed.
Alternatively, the CRDs can be removed manually.
kubectl delete crd kaepolicies.device.openfuyao.com
NOTE
After the operator is uninstalled, the driver may still exist on the host machine. If you want to remove it, update theenabledCleanupfield in values.yaml or kae-policy CR totruebefore uninstallation.driver:
enabled: true
enabledCleanup: true
Using the HPRE Accelerator in a Cluster
HPRE Device Resources
HPRE is a KAE Device Plugin that reports KAE HPRE devices on nodes to kubelet as openfuyao.com/kae.hpre resources. You can run the following command to view the number of devices on nodes in a cluster:
kubectl describe nodes <nodeName>
Output example
Allocatable:
cpu: 8
ephemeral-storage: 35858792389
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
hugepages-32Mi: 0
hugepages-64Ki: 0
memory: 16005200Ki
openfuyao.com/kae.hpre: 2 #check here
pods: 110
The preceding example indicates that there are two HPRE devices on the node.
Workload Configuration
Currently, KAE HPRE encryption and decryption support OpenSSL 1.1.1.1x asymmetric encryption and decryption. For services that use OpenSSL 1.1.1.1x encryption and decryption in the cluster, perform the following operations:
-
Edit the workloads that use KAE acceleration in the cluster, for example,
nginx_deployment.yaml.kubectl edit deployments nginx_deployment -n <namespace> -
Add the
resourcesfield to request KAE resources.resources:
requests:
openfuyao.com/kae.hpre: 1 -
Mount the OpenSSL configuration file to the container image.
volumeMounts:
- name: openssl-conf
mountPath: /<container_path>/openssl.cnf
volumes:
- name: openssl-conf
hostPath:
path: /<host_path>/openssl.cnf/<host_path>is the path of the host machine where the configuration file is stored, and/<container_path>is a path in the container.The
openssl.cnffile content is as follows:openssl_conf=openssl_def
[openssl_def]
engines=engine_section
[engine_section]
kae=kae_section
[kae_section]
engine_id=kae
dynamic_path=/usr/local/lib/engines-1.1/kae.so
KAE_CMD_ENABLE_ASYNC=1
KAE_CMD_ENABLE_SM3=1
KAE_CMD_ENABLE_SM4=1
default_algorithms=ALL
init=1You can also mount the preceding file to the container using a ConfigMap.
-
Set environment variables.
env:
- name: OPENSSL_CONF
value: /<container_path>/openssl.cnf -
Save the modification. The modification takes effect after the pod is rescheduled.