openFuyao Ray
Feature Overview
Ray is a distributed computing framework that supports function-level, on-demand scheduling of heterogeneous computing resources. It applies to general-purpose computing, intelligent computing, and hybrid scenarios combining both. It provides efficient and easy-to-use multi-language APIs to improve the duty cycle and optimize the comprehensive utilization of computing power. Ray supports multiple job forms, such as RayCluster, RayJob, and RayService. Multiple RayClusters are deployed in a Kubernetes cluster to process computing jobs of different tenants and applications. openFuyao Ray provides Ray cluster and job management capabilities. They help you reduce O&M costs and enhance cluster observability, fault diagnosis, and optimization practices. In addition, openFuyao Ray helps you build a computing power management solution based on the cloud-native architecture to improve computing power utilization.
Applicable Scenarios
Ray is widely used in the following scenarios: machine learning, hyperparameter optimization, big data processing, reinforcement learning, and model deployment.
Supported Capabilities
-
Resource management
- Allows users to create, query, remove, start, and terminate RayCluster, RayJob, and RayService resources, implementing flexible computing resource management.
- Allows users to create and modify RayCluster, RayJob, and RayService resources in file or text configuration mode to meet different deployment requirements.
- Displays RayCluster, RayJob, and RayService resource details, YAML files, and logs.
-
Global Ray resource monitoring
- Displays the numbers of active RayClusters, RayJobs, and RayServices and the total number of active Ray clusters.
- Displays the total physical and logical resources occupied by all Ray clusters, which are calculated based on the pod request values.
- Displays the statistics on the total physical and logical resources used by the Ray clusters, which are calculated based on both physical resource monitoring data and Ray-specific logical resource data.
Highlights
openFuyao Ray provides simple and efficient Ray resource management and global monitoring capabilities, supports convenient configuration and flexible scheduling of RayClusters, RayJobs, and RayServices, simplifies the computing resource management process, and improves cluster observability and computing power utilization.
Related Features
This feature depends on the monitoring capabilities provided by Prometheus.
Implementation Principles
Figure 1 Implementation principles
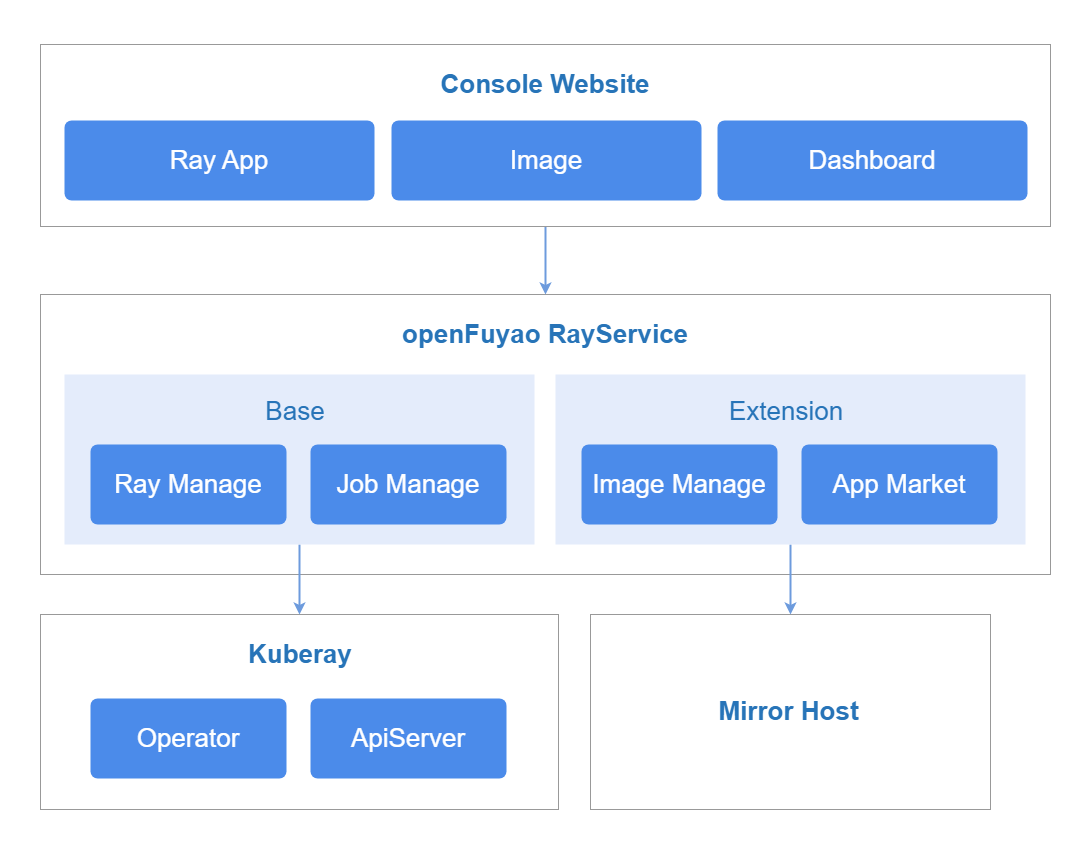
openFuyao Ray is structured into three service layers: frontend service, backend service, and component service.
Frontend Service
The ray-website provides visualized interfaces for management of RayCluster, RayJob, and RayService resources. This facilitates large-scale cluster management, and improves the visualized management capability for Ray computing tasks. It also integrates data visualization, and displays key monitoring information such as task execution status, resource usage, and scheduling logs.
Backend Service
The ray-service is deployed as a microservice to provide some core capabilities, including metric query as well as creation, query, deletion, start, and termination of RayCluster, RayJob, and RayService resources.
Component Service
-
KubeRay: KubeRay is an operator provided by the Ray community for Kubernetes. It manages Ray clusters through custom resource definitions (CRDs) of Kubernetes.
-
Prometheus: It collects monitoring data of Ray clusters, including key metrics such as the numbers of RayClusters, RayJobs, and RayServices as well as resource usage (CPU, GPU, and memory). It also stores the data for query and analysis.
-
Grafana: It provides visualized dashboards for the Ray cluster running state, computing resource usage, and task execution status based on the data collected by Prometheus.
Installation
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes 1.21 or later has been deployed.
- MindX DL 5.0.1 or later has been deployed.
Procedure
Deployment on the openFuyao Platform
- In the left navigation pane of the openFuyao platform, choose Application Market > Applications. The Applications page is displayed.
- Select Extension in the Type filter on the left to view all extensions. Alternatively, enter ray-package in the search box to search for the component.
- Click the ray-package card. The details page of the Ray extension is displayed.
- Click Deploy. The Deploy page is displayed.
- Enter the application name and select the desired installation version and namespace.
- Enter the values to be deployed in Values.yaml.
- Click OK.
- In the left navigation pane, click Extension Management to manage the Ray component.
Standalone Deployment
-
Obtain the Ray Helm package.
wget https://harbor.openfuyao.com/chartrepo/openfuyao-catalog/charts/ray-package-0.13.0.tgz -
Enter the values to be deployed in Values.yaml.
-
Configure
ray-service.grafana.grafana.ini.server.domainto specify the domain name or IP address for users to access Grafana. -
Set
ray-service.grafana.service.typetoNodePortto expose the service on all nodes through a specified port. -
Set
ray-service.grafana.service.nodePortto a port number within the30000-32767range. -
Set
ray-service.grafana.openFuyaoandray-website.openFuyaotofalse. -
Set
ray-website.enableOAuthtofalse. -
Set
ray-website.service.typetoNodePortto expose the service on all nodes through a specified port. -
Set
ray-website.service.nodePortto a port number within the30000-32767range. -
Configure
ray-website.backend.monitoringto point to thePrometheusaddress.http://<prometheus-service-name>.<namespace>.svc:<port>
-
-
Deploy the component using Helm.
tar -zxf ray-package-0.13.0.tgz
helm install openFuyao-ray -n default ./ray-package -
Verify the installation and access.
-
Ensure that openFuyao Ray has been successfully deployed.
kubectl get pods -n vcjob
kubectl get pods -n default -
Ensure that the service is exposed.
kubectl get svc -n default | grep ray-website -
Access the ray-website page.
http://<Node_IP>:<ray-website.service.nodePort>
NOTE
When accessing Grafana for the first time, use the default usernameadminand passwordadmin. After the login, change the password promptly to ensure security. -
Viewing the Overview
Prerequisites
The ray-package extension has been deployed in the application market.
Context
The Overview page displays information about all Ray applications, including:
- Numbers of active RayClusters, RayJobs, and RayServices, and the total number of all active Ray clusters.
- Total physical and logical resources of all Ray clusters, which are calculated based on the pod request values.
- The actual physical and logical resource usage of all Ray clusters, which are calculated based on both physical resource monitoring data and Ray-specific logical resource data.
Restrictions
None.
Procedure
-
In the left navigation pane of the openFuyao platform, choose Computing Power Optimization Center > openFuyao Ray > Overview. The Overview page is displayed.
Figure 2 Overview
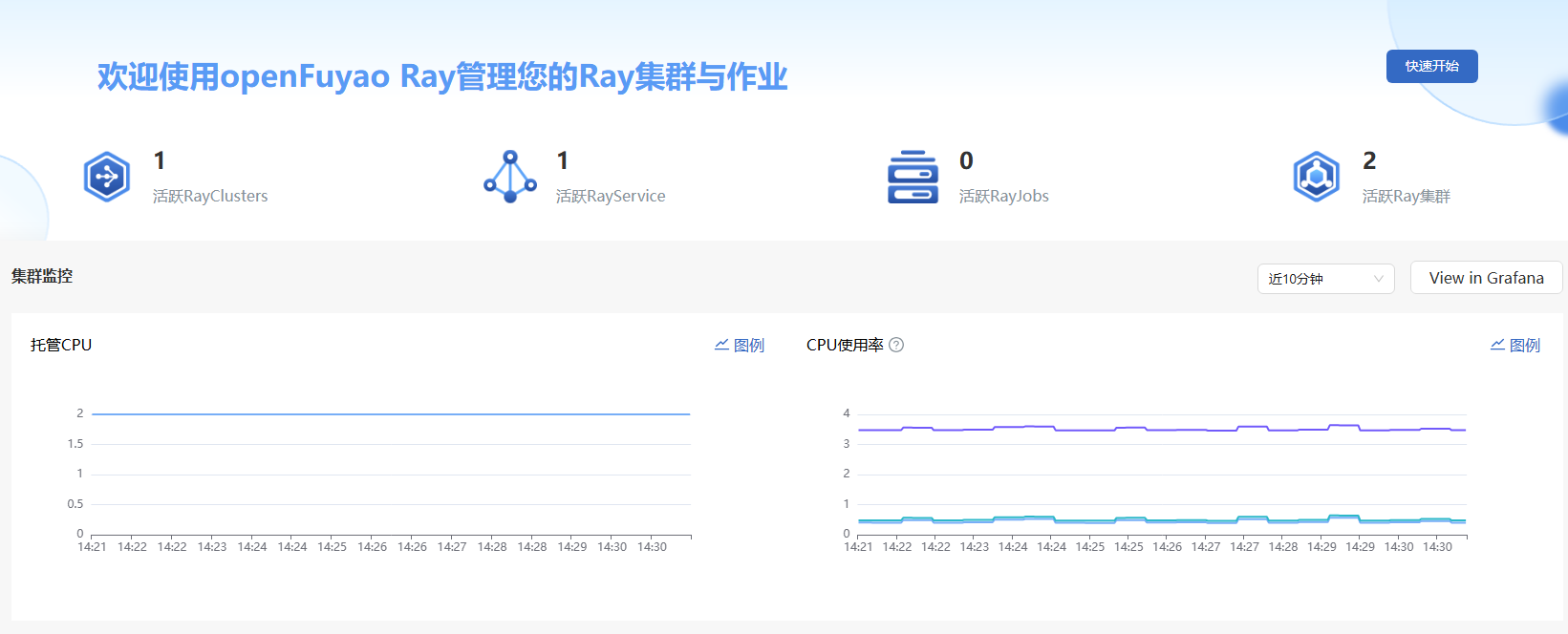
- (Optional) Select a time range: On the Overview page, you can filter Ray computing resources by time to view the status and usage of Ray computing resources in the last 10 minutes, 30 minutes, or 1 hour.
- View Ray resource monitoring data: The Overview page displays the numbers of active RayClusters, RayJobs, and RayServices, as well as the computing resource allocation and usage.
-
(Optional) Go to Grafana: On the Overview page, click View in Grafana on the right of the Cluster Monitoring section. On the Grafana monitoring panel that is displayed, you can view the detailed monitoring data of Ray computing clusters.
Using RayCluster
In the left navigation pane of the openFuyao platform, choose Computing Power Optimization Center > openFuyao Ray > RayCluster. The RayCluster page is displayed.
Figure 3 RayCluster
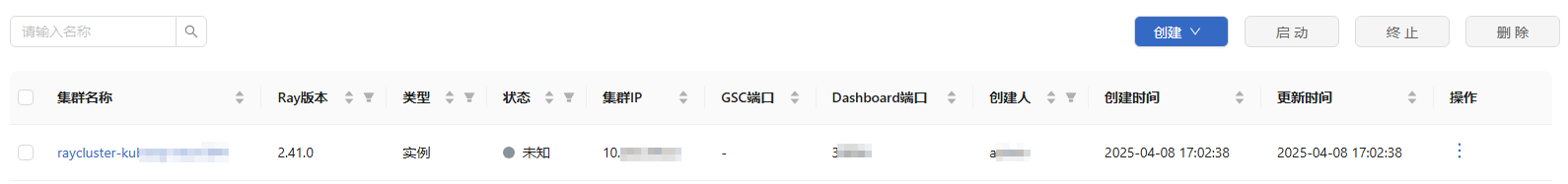
The RayCluster page supports the following functions:
- Fuzzy search by RayCluster name: Enter a partial or complete RayCluster name in the search box. The system automatically filters the matched RayCluster instances.
- List sorting: The RayCluster list can be sorted in ascending or descending order.
- Filtering: You can filter data by Ray version, resource type (template and instance), status, and creator.
- Resource management: You can create, query, remove, start, and terminate RayCluster resources.
Viewing RayCluster Details
Prerequisites
The ray-package extension has been deployed in the application market.
Context
You can view the basic information, YAML configuration, operation logs, and monitoring details of the current RayCluster.
Restrictions
None.
Procedure
-
On the RayCluster page, click any RayCluster in the Cluster name column. The RayCluster details page is displayed. This page supports the following functions:
-
On the Details page, you can view the basic information, algorithm framework, head node specifications and configurations, and worker node specifications of the RayCluster.
-
In the YAML tab, you can view and export the YAML configuration of RayCluster.
-
In the Logs tab, you can view RayCluster operation logs for debugging and troubleshooting.
-
-
Click Ray Dashboard. On the Ray Dashboard page that is displayed, you can view the task execution status, resource usage, and scheduling information of the cluster.
-
Click the drop-down list in the Operation column on the right. You can start, terminate, or remove a RayCluster as required.
Creating a RayCluster
Prerequisites
The ray-package extension has been deployed in the application market.
Context
When you need to run a Ray computing task, you need to create a RayCluster to automatically schedule computing resources in the cluster.
Restrictions
You must have the platform admin or cluster admin role.
Procedure
-
On the RayCluster list page, click Create on the right.
Figure 4 Creating a RayCluster
-
Select a creation method as required.
Figure 5 RayCluster Create Configuration
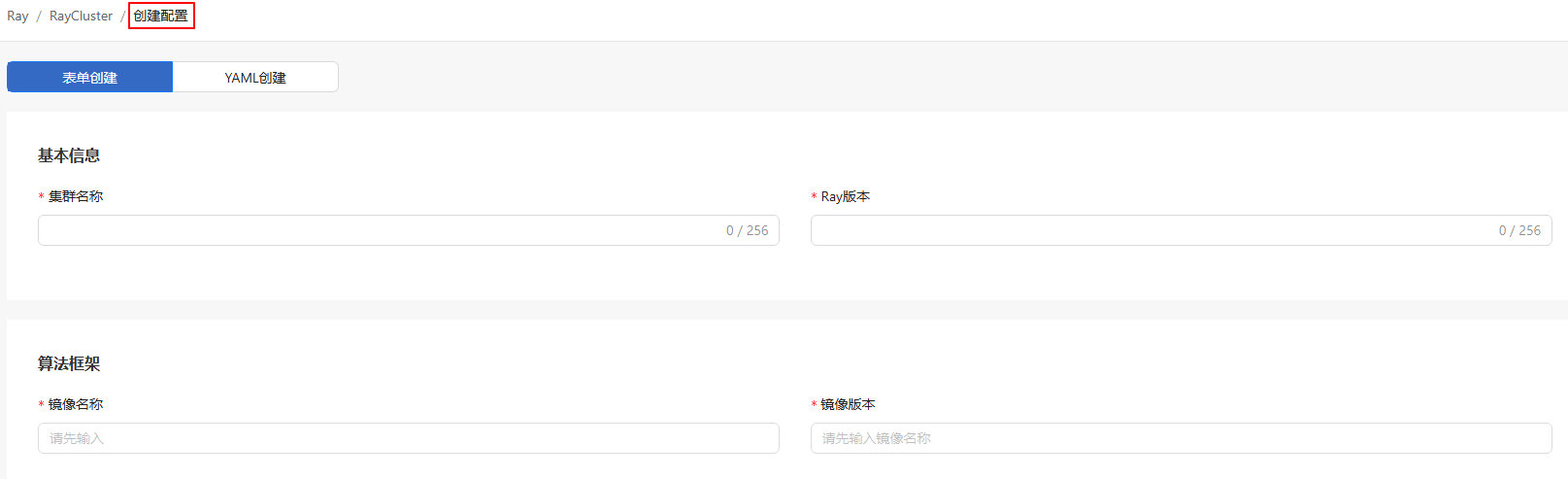
Table 1 Creation methods
Method Procedure Method 1 1. Select Create Configuration from the drop-down list.
2. Switch to the Form-based or YAML-based tab.Method 2 1. Select Upload Configuration from the drop-down list.
2. In the displayed Upload Configuration dialog box, click Select File to upload the YAML file that contains the RayCluster configuration.
3. Click Upload and Deploy. The RayCluster is created.-
Form-based: The underlying configuration is the same as that of the native YAML file of KubeRay. You can configure RayCluster parameters (such as the cluster name, image version, computing resource allocation, and number of worker replicas) in a visualized form. With this method, you do not need to manually edit YAML files.
- You can specify an open-source Ray image (for example,
docker.io/library/ray) in the image address. - You can specify an openFuyao-Ray image in the image address.
- You can specify a custom image in the image address. If additional dependencies (such as custom Python, VLLM, or specific hardware drivers) are required, you are advised to build a custom image based on the preceding images.
- You can specify an open-source Ray image (for example,
-
YAML-based: You can directly edit the YAML configuration file. This method applies to users who are familiar with RayCluster CRD specifications, allowing customization of advanced parameters.
-
-
Click Create or Create and Start to complete the creation. For a sample YAML, see Example YAML for Creating a RayCluster.
Removing a RayCluster
Prerequisites
The ray-package extension has been deployed in the application market.
Context
If a RayCluster is no longer needed or you want to free up computing resources, you can remove the RayCluster and clear its head and worker nodes as well as related resources to prevent unnecessary resource occupation.
Restrictions
-
You must have the platform admin or cluster admin role.
-
Removal is allowed for RayClusters in states other than Running.
Procedure
-
Removing RayClusters in batch
- In the RayCluster list, select the RayClusters to be removed.
- Click Delete on the right of the list.
- In the displayed dialog box, click OK. The selected RayClusters are removed.
-
Removing a single RayCluster
-
Method 1: On the RayCluster list page, click
in the Operation column.
Method 2: On the RayCluster details page, click Operation on the right.
-
Select Delete from the drop-down list.
-
In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
-
Related Operations
You can click Start or Terminate on the right of the list page, or click and select Start or Terminate in the Operation column on the details page to perform RayCluster-related operations as required.
Table 2 Related operations
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Start | If a RayCluster is in a terminated or unstarted state, you can start it to restore the computing capability so that it can run RayJob and RayService tasks again and schedule resources in the cluster. |
| Stop | When computing tasks are completed or no longer needed, you can terminate the RayCluster to free up computing resources and optimize cluster utilization, preventing unnecessary resource occupation. |
Follow-up Operations
To create, query, remove, start, and terminate RayServices and RayJobs, refer to, refer to the procedure of RayCluster-related operations.
Appendixes
Example YAML for Creating a RayCluster
The following is an example YAML file for creating a RayCluster.
apiVersion: ray.io/v1
kind: RayCluster
metadata:
name: raycluster-kuberay-test-x86
spec:
rayVersion: '2.41.0'
headGroupSpec:
serviceType: NodePort
rayStartParams:
num-cpus: "0" # not allowed
template:
spec:
volumes:
- name: ray-logs
emptyDir: {}
- name: parsers
configMap:
name: fluentbit-config
items:
- key: parsers.conf
path: parsers.conf
- name: fluentbit-config
configMap:
name: fluentbit-config
items:
- key: fluent-bit.conf
path: fluent-bit.conf
- name: scripts-volume
configMap:
name: fluentbit-config
items:
- key: script.lua
path: script.lua
containers:
- name: ray-head
image: docker.io/rayproject/ray:2.41.0 # In the Arm architecture, the tag is 2.41.0-aarch64.
resources:
requests:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "500Mi"
limits:
cpu: "1000m"
memory: "2000Mi"
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
name: gcs-server
- containerPort: 8265
name: dashboard
- containerPort: 10001
name: client
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /tmp/ray
name: ray-logs
- name: fluentbit # To enable Loki, this container must be added.
image: docker.io/fluent/fluent-bit:2.0.5
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "1G"
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "1G"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /tmp/ray
name: ray-logs
- mountPath: /etc/fluent-bit/conf/parsers.conf
subPath: parsers.conf
name: parsers
- mountPath: /fluent-bit/etc/fluent-bit.conf
subPath: fluent-bit.conf
name: fluentbit-config
- name: scripts-volume
mountPath: /etc/fluent-bit/scripts/
env:
- name: RAY_JOB_NAME
value: raycluster-kuberay-test-x86 # The value must correspond to the name of the RayCluster, which is the value of metadata.name.
workerGroupSpecs:
- replicas: 1
minReplicas: 0
maxReplicas: 2
groupName: workergroup
rayStartParams: {}
template:
spec:
volumes:
- name: ray-logs
emptyDir: {}
- name: parsers
configMap:
name: fluentbit-config
items:
- key: parsers.conf
path: parsers.conf
- name: fluentbit-config
configMap:
name: fluentbit-config
items:
- key: fluent-bit.conf
path: fluent-bit.conf
- name: scripts-volume
configMap:
name: fluentbit-config
items:
- key: script.lua
path: script.lua
containers:
- name: ray-worker
image: docker.io/rayproject/ray:2.41.0 # In the Arm architecture, the tag is 2.41.0-aarch64.
resources:
requests:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "500Mi"
limits:
cpu: "1000m"
memory: "2000Mi"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /tmp/ray
name: ray-logs
- name: fluentbit
image: docker.io/fluent/fluent-bit:2.0.5
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "1G"
limits:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "1G"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /tmp/ray
name: ray-logs
- mountPath: /etc/fluent-bit/conf/parsers.conf
subPath: parsers.conf
name: parsers
- mountPath: /fluent-bit/etc/fluent-bit.conf
subPath: fluent-bit.conf
name: fluentbit-config
- name: scripts-volume
mountPath: /etc/fluent-bit/scripts/
env:
- name: RAY_JOB_NAME
value: raycluster-kuberay-test-x86 # The value must correspond to the name of the RayCluster, which is the value of metadata.name.